一,SpringMVC的常用注解
一,RequestMaping
作用:为类和方法提供映射关系
源码:
//ElementType.METHOD作用于方法,ElementType.TYPE作用于类
@Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)//运行级别
@Documented//它代表着此注解会被javadoc工具提取成文档
@Mapping
public @interface RequestMapping {
String name() default "";
//path和value作用是一样的,声明映射路径
@AliasFor("path")
String[] value() default {};
@AliasFor("value")
String[] path() default {};
//声明请求类型枚举数组类型
RequestMethod[] method() default {};
//声明映射参数
String[] params() default {};
//声明请求头部信息
String[] headers() default {};
//声明数据请求提交的类型
String[] consumes() default {};
//声明数据请求返回的数据类型
String[] produces() default {};
}
一,RequestMapping的属性:
1,path和value
说明资源映射的路径
2,RequestMethod
说明请求的类型它是一个枚举类,总共有八种请求方式
public enum RequestMethod {
GET,
HEAD,
POST,
PUT,
PATCH,
DELETE,
OPTIONS,
TRACE;
private RequestMethod() {
}
3,param
说明请求头需要声明的参数,匹配则请求成功,反之失败
4,headers
说明请求需要的请求头部信息,匹配则请求成功,反之失败
5,consumes和produces
声明请求和响应的数据类型
数据类型:
常见的媒体格式类型如下:
- text/html : HTML格式
- text/plain :纯文本格式
- text/xml : XML格式
- image/gif :gif图片格式
- image/jpeg :jpg图片格式
- image/png:png图片格式
以application开头的媒体格式类型:
- application/xhtml+xml :XHTML格式
- application/xml : XML数据格式
- application/atom+xml :Atom XML聚合格式
- application/json : JSON数据格式
- application/pdf :pdf格式
- application/msword : Word文档格式
- application/octet-stream : 二进制流数据(如常见的文件下载)
- application/x-www-form-urlencoded : <form encType=””>中默认的encType,form表单数据被编码为key/value格式发送到服务器(表单默认的提交数据的格式)
二,RequestMapping请求参数的绑定
绑定参数名或者提供的input的name必须要和方法的参数名保持一致,这样才能形成映射关系
一,get请求的绑定
标签:
<a href="/wql?name=10" >a</a>
类:
@Controller
public class test1 {
@RequestMapping(path = "/wql")
public void enter(String name){//a标签的参数name和方法的形参形成对应关系
System.out.println(name);
}
}
输出结果:10
二,post请求绑定
标签:
<form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/wql">
账号:<input type="text" name="account">
密码:<input type="text" name="password">
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</form>
类:
@Controller
public class test1 {
@RequestMapping(path = "/wql")
public void enter(String account,String password){
System.out.println(account+"\n"+password);
}
}
三,绑定bean对象
bean对象类:
@Controller
public class WQL1 {
String account;
String password;
public String getAccount() {
return account;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setAccount(String account) {
this.account = account;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
}
标签:
<form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/wql">
<%--名称和bean实体类中的属性名一致--%>
账号:<input type="text" name="account">
密码:<input type="text" name="password">
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</form>
RequestMapping:
@Controller
public class test1 {
@RequestMapping(path = "/wql")
public void enter(WQL1 wql1){//提交的数据和bean对象的属性自动产生映射
System.out.println(wql1.account+"\n"+wql1.password);
}
}
三,绑定集合
实体类:
Controller
public class WQL1 {
String account;
String password;
ArrayList<String> list;
Map<String,String> map;
public ArrayList<String> getList() {
return list;
}
public void setList(ArrayList<String> list) {
this.list = list;
}
public Map<String, String> getMap() {
return map;
}
}
表单:
<form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/wql">
账号:<input type="text" name="account">
密码:<input type="text" name="password">
name:<input type="text" name="list[0]">
map:<input type="text" name="map['age']">
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</form>
Requestmapping:
@Controller
public class test1 {
@RequestMapping(path = "/wql")
public void enter(WQL1 wql1){
System.out.println(wql1.account+"\n"+wql1.password+"\n"+ wql1.list.get(0)+"\n"+wql1.map.get("age"));
}
}
二,RequestParam
作用:用于获取传入参数的值,之前获取参数的值形参的名称必须要和表单的名称一致,通过RequestParam名称不需要一致
源码:
@Target({ElementType.PARAMETER})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface RequestParam {
//name和value一样,输入映射的名称,必须要和表单的名称一致
@AliasFor("name")
String value() default "";
@AliasFor("value")
String name() default "";
//参数是否必须
boolean required() default true;
String defaultValue() default "\n\t\t\n\t\t\n\ue000\ue001\ue002\n\t\t\t\t\n";
}
属性:
- name和value:输入映射的名称,必须和表单的name一致
-
required:是否参数必须
例:
<form action="/wql1">
<input type="text" name="name" >
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</form>
@Controller
public class test2 {
@RequestMapping(path = "/wql1")
public void wql(@RequestParam(value = "name") String a){
System.out.print(a);
}
三,RequestHeader和CookieValue
RequestHeader:获取请求头部信息
CookieValue:获取Cookie信息
RequestHeader源码:
public @interface RequestHeader {
//name和value声明请求头的key
@AliasFor("name")
String value() default "";
@AliasFor("value")
String name() default "";
//是否必须要请求头部信息
boolean required() default true;
String defaultValue() default "\n\t\t\n\t\t\n\ue000\ue001\ue002\n\t\t\t\t\n";
}
CookieValue源码:
public @interface CookieValue {
//name和value声明Cookie的key
@AliasFor("name")
String value() default "";
@AliasFor("value")
String name() default "";
//是否必须要Cookie信息
boolean required() default true;
String defaultValue() default "\n\t\t\n\t\t\n\ue000\ue001\ue002\n\t\t\t\t\n";
}
例:
@Controller
public class test2 {
@RequestMapping(path = "/wql1")
//把头部user-agent的值赋值给a变量,Cookie的JSESSIONID赋值给变量b
public void wql(@RequestHeader(value = "user-agent") String a,@CookieValue(value ="JSESSIONID")String b){
System.out.print(a+"\n"+b);}
}
四,PathVariable
PathVariable作用:用于绑定url占位符 例:/wql/{id} id获取任意的字符,通过@PathVariabl(name="id") String a 赋值给字符串a
PathVariable是SpringMVC支持Rest风格URL的重要标志
PathVariable源码:
@Target({ElementType.PARAMETER})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface PathVariable {
//name和value声明匹配的占位符ID
@AliasFor("name")
String value() default "";
@AliasFor("value")
String name() default "";
//是否必须要占位符
boolean required() default true;
}
例:
@Controller
public class test3 {
@RequestMapping(value = "/ww/{id}")
public void c(@PathVariable(value = "id")String a){
System.out.print(a);
}
}
五,RequestBoby和ResponseBody
RequestBody:将表单数据作为一个整体转换为json数据,赋值给变量
ResponseBody:将对象类型数据和其他数据类型转换为json类型进行返回响应
RequestBody源码:
@Target({ElementType.PARAMETER})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface RequestBody {
boolean required() default true;//唯一一个参数,是否必须要进行json数据获取
}
ResponseBody源码:
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface ResponseBody {
}//无属性
例:
<form action="/wql2" method="post">
<input type="text" name="name" >
<input type="text" name="password" >
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</form>
public class test4 {
@RequestMapping(value = "/wql2")
public void aas(@RequestBody String body){
System.out.print(body);
}
结果: name=wql&password=123456
二,SpringMVC中使用域对象
在SpringMVC中使用域对象有四种方式:
- 使用原生Servlet对象
- 使用ModelandView对象
- 使用Map集合
- Mode1对象
一,SpringMVC获取Servlet原生API
在SpringMVC中Hander方法形参中可以接收的Servlet类型的参数:
- HttpServletRequest
- HttpServletResponse
- HttpSession
- Locale
- InputStream
- OutputStream
- writer
- Reader
可以使用原生的HttpSession和HttpServletRequest获取域对象
例:
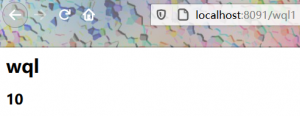
@RequestMapping(path = "/wql1")
public String wql(HttpSession session, HttpServletRequest request){
session.setAttribute("name","wql");
request.setAttribute("age","10");
return "seccion";
}
}
jsp:
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>${sessionScope.get("name")}</h1>
<h2>${requestScope.get("age")}</h2>
</body>
</html>
二,ModelandView
ModelandView:Model设置域,View设置视图
构造ModelAndView对象当控制器处理完请求时,通常会将包含视图名称或视图对象以及一些模型属性的ModelAndView对象返回到DispatcherServlet。
因此,经常需要在控制器中构造ModelAndView对象。
ModelAndView类提供了几个重载的构造器和一些方便的方法,让你可以根据自己的喜好来构造ModelAndView对象。这些构造器和方法以类似的方式支持视图名称和视图对象。
通过ModelAndView构造方法可以指定返回的页面名称,也可以通过setViewName()方法跳转到指定的页面 , 使用addObject()设置需要返回的值,addObject()有几个不同参数的方法,可以默认和指定返回对象的名字。
构造方法:
ModelAndView() //默认构造函数豆式的用法:填充bean的属性,而不是将在构造函数中的参数。 ModelAndView(String viewName) //方便的构造时,有没有模型数据暴露。 ModelAndView(String viewName, Map model) //给出创建一个视图名称和模型新的ModelAndView。 ModelAndView(String viewName, String modelName, Object modelObject) //方便的构造采取单一的模式对象。 ModelAndView(View view) //构造方便在没有模型数据暴露。 ModelAndView(View view, Map model) //创建给定一个视图对象和模型,新的ModelAndView。 ModelAndView(View view, String modelName, Object modelObject) //方便的构造采取单一的模式对象。
类方法:
ModelAndView addAllObjects(Map modelMap) //添加包含在所提供的地图模型中的所有条目。 ModelAndView addObject(Object modelObject) //添加对象使用的参数名称生成模型。 ModelAndView addObject(String modelName,ObjectmodelObject) //对象添加到模型中。 void clear() //清除此ModelAndView对象的状态。 Map getModel() //返回的模型图。 protectedMap getModelInternal() //返回的模型图。 ModelMap getModelMap() //返回底层ModelMap实例(从不为null)。 View getView() //返回View对象,或者为null,如果我们使用的视图名称由通过一个ViewResolverDispatcherServlet会得到解决。 String getViewName() //返回视图名称由DispatcherServlet的解决,通过一个ViewResolver,或空,如果我们使用的视图对象。 boolean hasView() //指示此与否的ModelAndView有一个观点,无论是作为一个视图名称或作为直接查看实例。 boolean isEmpty() //返回此ModelAndView对象是否为空,即是否不持有任何意见,不包含模型。 boolean isReference() //返回,我们是否使用视图的参考,i.e. void setView(Viewview) //设置此ModelAndView的视图对象。 void setViewName(StringviewName) //此ModelAndView的设置视图名称,由通过一个ViewResolverDispatcherServlet会得到解决。 String toString() //返回这个模型和视图的诊断信息。 boolean wasCleared()?? //返回此ModelAndView对象是否为空的调用的结果,以清除(),即是否不持有任何意见,不包含模型。
例:
@Controller
public class test2 {
@RequestMapping(path = "/wql1")
//使用ModelandView需要将ModelandView对象返回
public ModelAndView wql(){
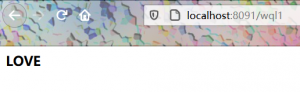
ModelAndView a=new ModelAndView();
a.addObject("name","LOVE");
a.setViewName("seccion");
return a;
}
}
jsp页面:
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2>${name}</h2>
</body>
</html>
结果:ModelandView页面的跳转是服务器内部的转发,url地址并不会发生改变
三,Mode1
源码:
public interface Model {
//添加域
Model addAttribute(String var1, Object var2);
Model addAttribute(Object var1);
//将K-V存储在集合中进行存储
Model addAllAttributes(Collection<?> var1);
Model addAllAttributes(Map<String, ?> var1);
Model mergeAttributes(Map<String, ?> var1);
boolean containsAttribute(String var1);
Map<String, Object> asMap();
}
四,普通的Map集合
在形参中加入普通的Map集合,底层会把Map集合转化为ModleandView中的ModelMap集合
三,文件的上传
文件的上传的jar包:文件上传依赖包
- commons-fileupload
- commons-io
一,Servlet的传统文件上传
不多说
@Controller
public class test8 {
@RequestMapping(value = "/FQlove")
public String addddd(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
//上传位置
String path = request.getServletContext().getRealPath("/wqlfq");
File file = new File(path);
if(!file.exists()){
file.mkdir();
}
//获取request的上传文件项
DiskFileItemFactory diskFileItemFactory = new DiskFileItemFactory();
ServletFileUpload servletFileUpload =new ServletFileUpload(diskFileItemFactory);
//解析request
List<FileItem> item=servletFileUpload.parseRequest(request);
//遍历
for(FileItem item1 : item){
//判断当前FileItem是否是上传文件项
if(item1.isFormField()){
//它为true说明是普通表单项
}else {
//上传文件项
String name = item1.getName();
System.out.print(name);
item1.write(new File(path,name));
}
}
System.out.print("文件上传!!!");
return "seccion";
}
}
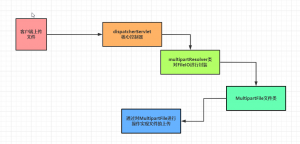
二,SpringMVC实现文件的上传
SpringMVC的文件上传依赖于MultipartFile的类,它把上传的File文件封装成了MultipartFile类对象,通过操作MultipartFile实现文件的上传
底层原理:
MultipartFile源码:
public interface MultipartFile extends InputStreamSource {
//获取请求url名称
String getName();
//获取上传文件的名称
String getOriginalFilename();
//获取文件的类型
String getContentType();
//判断是否为空
boolean isEmpty();
//获取文件大小
long getSize();
//缓冲数组
byte[] getBytes() throws IOException;
//获取InputStream文件输入流
InputStream getInputStream() throws IOException;
//直接对象上传文件进行复制的方法
void transferTo(File var1) throws IOException, IllegalStateException;
}
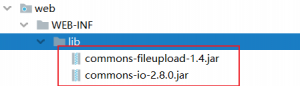
一,环境准备
1,将依赖包放入web下的lib目录中
2,在SpringMVC中配置multipartResolver
<bean name="multipartResolver"
class="org.springframework.web.multipart.commons.CommonsMultipartResolver">
<!--上传文件的最大大小,单位为字节 -->
<property name="maxUploadSize" value="17367648787"/>
<!-- 上传文件的编码 -->
<property name="defaultEncoding" value="UTF-8"/>
</bean>
二,SpringMVC文件上传(1)
jsp表单:inpu的type必须为file
<form action="/fs1" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data">
选择上传文件:<input type="file" name="upload">
<input type="submit" value="上传">
</form>
上传代码:
@Controller
public class fs1 {
@RequestMapping("/fs1")
public String va(MultipartFile upload, HttpServletRequest request) throws IOException {
//在项目路径下,创建文件夹
System.out.println("方式1!!!");
String path = request.getServletContext().getRealPath("fs1");
String name = upload.getOriginalFilename();//获取上传的文件名
//判断文件是否存在,不存在创建
File file = new File(path);
if(!file.exists()){
file.mkdir();
}
//获取上传的文件输入流
InputStream inputStream = upload.getInputStream();
//获取文件的输出流
OutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream(new File(file,name));
//文件的复制
int a=0;
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
while ((a=inputStream.read(bytes))!=-1){
outputStream.write(bytes,0,a);
}
inputStream.close();
outputStream.close();
return "seccion";
}
}
文件的上传目录:为当前项目目录下
三,SpringMVC文件上传(2)
@RequestMapping(value = "/we",method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String vc(@RequestParam(value = "upload") MultipartFile upload, HttpServletRequest request) throws IOException {
String path = request.getServletContext().getRealPath("photo");
System.out.println(path);
File file = new File(path);
if(!file.exists()){
file.mkdir();
}
//方法直接打印
upload.transferTo(new File(file,upload.getOriginalFilename()));
return "seccion";
}
四,restful风格
概述:
RESTful也称之为REST(Representational State Transfer),可以理解为一种软件架构风格或者是设计风格
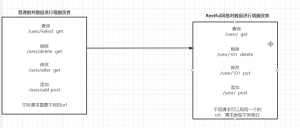
简单来说,RESTful风格就是把请求参数变成请求路径的一种风格
举个例子
而采用RESTful风格后,URL地址请求就会变成
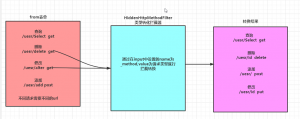
注意:在ajax中它可以发生8中不同的请求,可以对应RequestMapping的值,当不使用ajax请求,普通的from表单只能发送两种请求(post,get),并不能发送请求类型请求,我们就需要一个类型转化的拦截器,进行中间的转化拦截,实现不同请求的rest风格实现
一,普通表单提交实现Restful风格
普通表单只能发送两种请求,我们需要在中间做类型的转化拦截器,把请求拦截(HiddenHttpMethodFilter)进行类型转化
HiddenHttpMethodFilter类型转换拦截器源码:
ublic class HiddenHttpMethodFilter extends OncePerRequestFilter {
public static final String DEFAULT_METHOD_PARAM = "_method";
//1,通过这个固定name为键,所以表单所有put和delete是需要讲name设置为_method,值为具体的请求类型
private String methodParam = "_method";
public HiddenHttpMethodFilter() {
}
public void setMethodParam(String methodParam) {
Assert.hasText(methodParam, "'methodParam' must not be empty");
this.methodParam = methodParam;
}
//3,
protected void doFilterInternal(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain filterChain) throws ServletException, IOException {
HttpServletRequest requestToUse = request;
//判断表单类型是否为post类型,为post就执行,假如为get就直接跳过不就行转化
if ("POST".equals(request.getMethod()) && request.getAttribute("javax.servlet.error.exception") == null) {
//接收input name参数的值
String paramValue = request.getParameter(this.methodParam);
if (StringUtils.hasLength(paramValue)) {
//讲值赋值给请求,就行请求类型转换
requestToUse = new HiddenHttpMethodFilter.HttpMethodRequestWrapper(request, paramValue);
}
}
filterChain.doFilter((ServletRequest)requestToUse, response);
}
private static class HttpMethodRequestWrapper extends HttpServletRequestWrapper {
private final String method;
//2,获取参数name为method的值
public HttpMethodRequestWrapper(HttpServletRequest request, String method) {
super(request);
//转化成大写
this.method = method.toUpperCase(Locale.ENGLISH);
}
//将大小后的method返回
public String getMethod() {
return this.method;
}
}
}
在web.xml中配置HiddenHttpMethodFilter:
<filter>
<filter-name>hiddenHttpMethodFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.HiddenHttpMethodFilter</filter-class>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>hiddenHttpMethodFilter</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
例:使用put请求
<form>
<!--必须在name中指定_method,值为请求类型,底层提供参数来获取类型-->
<input type="hidden" name="_method" value="put">
<input type="submit" value="提交put请求">
</form>
代码:
@Controller
public class tt {
@RequestMapping(value = "/wq",method = RequestMethod.PUT )
public String f(HttpServletRequest request){
//获取请求类型
System.out.println(request.getMethod());
return "seccion";
}
}
一,Ajax实现Restful风格
使用Ajax就不需要中间的拦截器了,业务Ajax可以提交多种不同类型的请求
//使用RESTful风格 @RequestMapping("/user/{id}") @ResponseBody public User selectUser(@PathVariable("id") String id){ //查看数据的接收 System.out.println("id->"+id); User user = new User(); //模拟根据id查询出到用户对象数据 if (id.equals("1234"))user.setUserName("tom"); return user; }
jsp: <%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %> <html> <head> <title>RESTful测试</title> <script src="http://libs.baidu.com/jquery/1.11.3/jquery.min.js"></script> <script type="text/javascript"> function search() { //获取输入的查询编号 var id = $("#number").val(); $.ajax({ url:"${pageContext.request.contextPath}/users/user/"+id, type:"GET", //定义回调响应的数据格式为JSON字符串 dataType:"JSON", success:function (data) { if (data.userName != null) { alert("您查询的用户:"+data.userName); }else { alert("没有查找到id为:"+id+"的用户") } } }); } </script> </head> <body> <form> 编号: <input type="text" name="number" id="number"> <input type="button" value="确定" onclick="search()"> </form> </body> </html
五,拦截器
一,拦截器和过滤器的区别
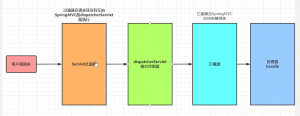
过滤器是Servlet配置的,它直接作用在Servlet上,拦截器是SpringMVC提供的在请求交由dispatcherServlet控制
过滤器的优先级高于拦截器
二,拦截器的实现方式
自定义拦截器主要有两种实现方式:
- 实现HandlerInterceptor接口
- 继承HandlerInterceptorAdapter适配器类
HandlerInterceptorAdapter和HandlerInterceptor的关系:HandlerInterceptorAdapter实现了HandlerInterceptor类,并对HandlerInterceptor接口方法进行了初始化
![]()
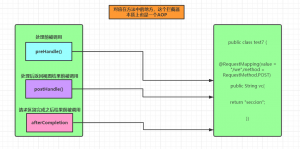
拦截器的三个主要方法:
1,preHandle():这个方法在handler处理器处理请求之前被调用,它的返回值为Boolean当拦截请求之后需要处理器去处理就返回true,不需要就返回false
2,postHandle():这个方法在处理器处理为请求逻辑之后,但DispatcherServlet控制器并没有返回结果时调用
3,afterCompletion():在DispatcherServlet完成处理好请求后被调用
三,拦截器的配置
拦截器在SpringMVC的配置文件中配置
1,方式1
<mvc:interceptors>
<!--拦截的class,默认路径tt类下的所有请求-->
<bean class="com.fq.tt"></bean>
</mvc:interceptors>
2,方式2
<mvc:interceptors>
<!--这种方式拦截器上必须加注解@Component-->
<ref bean="tt"></ref>
</mvc:interceptors>
3,方式3
<mvc:interceptors>
<mvc:interceptor>
<!--拦截的类-->
<bean></bean>
<!--类下要拦截的请求,默认全部请求-->
<mvc:mapping path="/"/>
<!--要放行的请求-->
<mvc:exclude-mapping path=""/>
</mvc:interceptor>
</mvc:interceptors>





Comments | NOTHING