一,Stream和ParallelStream
串行流(Stream)和并行流(parallelStream)的异同:
- 同:在API的使用上,两个没有差别
- 异:串行Stream在单线程进行操作,并行Stream在多线程进行操作,在效率上并行流要高
一,获取并行流的两种方式
- 方式一:直接获取并行parallelStream流
- 方式二:将串行流转成并行流
//方式一:通过集合直接获取
List<String> list = Arrays.asList("wql","kxj","fq","luoqin");
Stream s1 = list.parallelStream();
//方式二:通过串行流转化为并行流
Stream s2 = Arrays.stream(new String[]{"wql","kxj","fq","luoqin"});
s2.parallel();
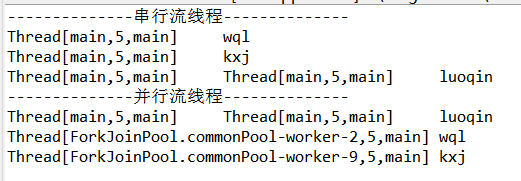
例:线程对比
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list = Arrays.asList("wql","kxj","fq","luoqin");
//1,串行流
System.out.println("--------------串行流线程--------------");
list.stream()
.filter((x) ->{
System.out.print(Thread.currentThread()+"\t");
return x.length()>2;})
.forEach(System.out::println);
//2,并行流
System.out.println("--------------并行流线程--------------");
list.stream()
.parallel()
.filter((x) ->{
System.out.print(Thread.currentThread()+"\t");
return x.length()>2;})
.forEach(System.out::println);
}
二,处理效率对比
对for循环,串行流,并行流分别从0到5亿进行递加,看最后的执行时间
public static void main(String[] args) {
for_test();
stream_test();
parallelstream_test();
}
static final int max = 500000000; //五亿
//1,循环五亿累加
public static void for_test() {
int sum = 0;
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
for(int a=0,maxnum=max;a<maxnum;a++) {
sum+=a;
}
System.out.println("For:"+(System.currentTimeMillis()-begin)+"毫秒");
}
//2,stream流五亿累加
public static void stream_test() {
int sum = 0;
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
LongStream.rangeClosed(0, max).reduce((x,y) -> x+y);
System.out.println("Stream:"+(System.currentTimeMillis()-begin)+"毫秒");
}
public static void parallelstream_test() {
int sum = 0;
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
LongStream.rangeClosed(0, max).parallel().reduce((x,y) -> x+y);
System.out.println("parallelStream:"+(System.currentTimeMillis()-begin)+"毫秒");
}
结果:
For:135毫秒 Stream:215毫秒 parallelStream:118毫秒
三,parallelStream的线程安全问题解决
线程安全问题演示:使用并行流将元素添加到集合中
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
IntStream.rangeClosed(0, 200)
.parallel()
.forEach(i -> list.add(i));
System.out.print(list.size());
}
结果:200个数字并没有完全添加到集合中
194
四种解决方案:
- 使用synchronized同步代码块
- 加入lock锁
- 使用线程安全的集合进行添加
- 使用collector方法避免线程安全问题
方案一:synchronized同步代码块
Object j = new Object();
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
IntStream.range(0, 200)
.parallel()
.forEach(i -> {
synchronized(j) {
list.add(i);
}});
System.out.print(list.size());
方案二:lock锁
Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
IntStream.range(0, 200)
.parallel()
.forEach(i -> {
lock.lock();
list.add(i);
lock.unlock();
});
System.out.print(list.size());
方案三:使用线程安全的集合
ConcurrentLinkedQueue<Integer> con = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue<>();
IntStream.range(0, 200)
.parallel()
.forEach(i -> {
con.add(i);
});
System.out.print(con.size());
方案四:collector方法避免线程安全
List<Integer> list =IntStream.range(0, 200) .parallel() .boxed()//Stream组成的这个流的元素 .collect(Collectors.toList()); System.out.print(list.size());
parallelStream总结:
- parallelStream是线程不安全的
- parallelStream适合于场景是CPU密集型的操作,做到尽量发挥CPU的利用率,如果本身电脑CPU的负载很大,就会起反作用
- 磁盘I/O、网络I/O等IO操作较少消耗CPU资源,一般并行流不适用这种I/O密集型操作,如:使用并行流大批量消息推送,涉及到大量I/O,速度会慢很多
- 使用ParallelStream并行流无法保证元素的顺序,因为是多线程操作
二,Fork/Join框架
一, Fork/Join框架介绍
parallelStream并行流底层使用的就是Fork/Join框架,这个框架在JDK1.7被引入,Fork/Join框架可以将一个大任 务拆分为很多个小任务来进行异步处理
Fork/Join框架底层引用了大数据中的Map/Reduce思想,对任务进行拆分/整合,分而治之处理任务
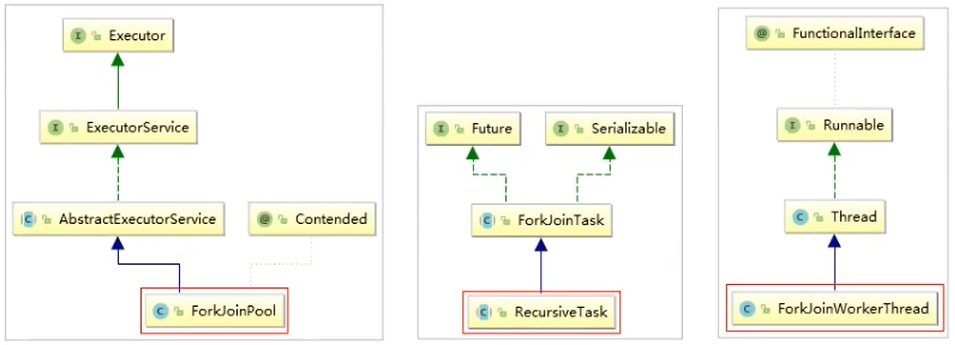
Fork/join框架主要包含三个模块:
- 线程池:ForkJoinPool
- 任务对象:ForkJoinTask
- 执行任务的线程:ForkJoinWorkThread
二,Fork/Join框架原理
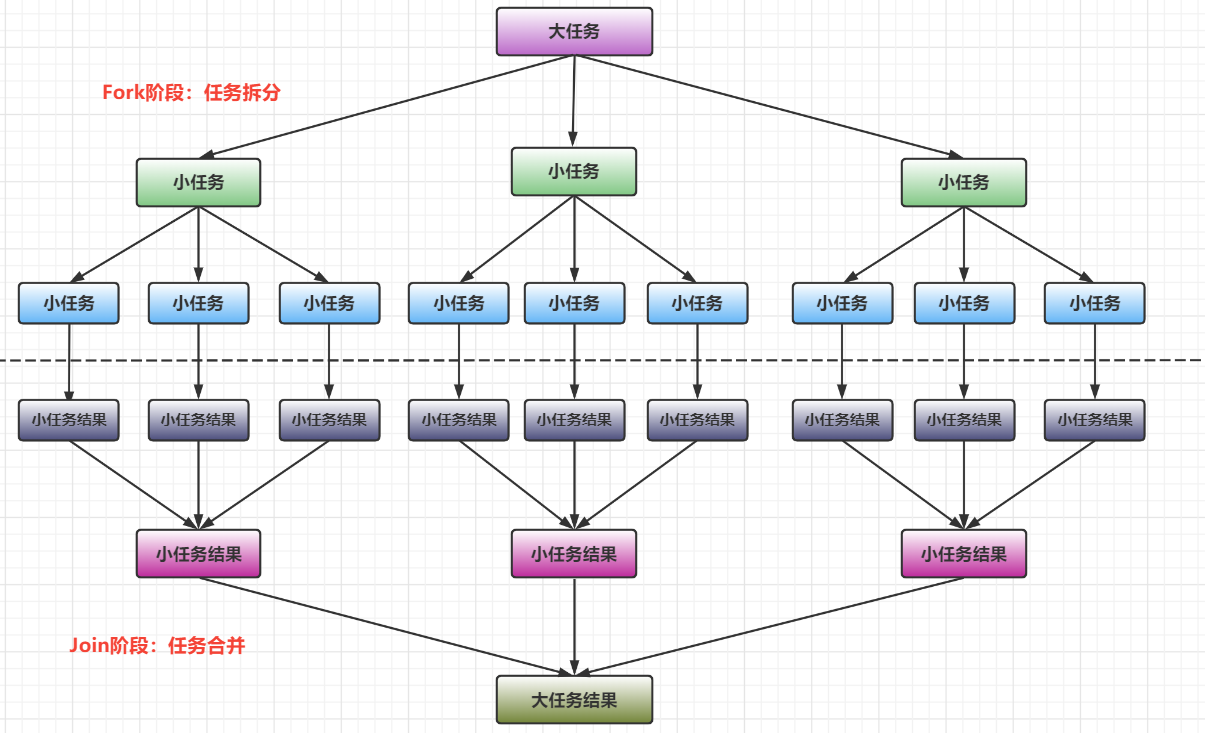
- 分治法:拆分/合并
- 任务窃取算法
一,分治法
ForkJoinPool主要用来使用分治法来解决问题
分治法两阶段:
- Fork阶段:任务拆分
- Join阶段:任务合并
分治法和快速排序算法很相似,ForkJoinPool需要使用相对少的线程来处理大量的任务,比如要对1200万个数据进行排序,那么将任务分割成三个400万的排序任务和针对这三组400万数据的合并任务,以此类推,对于400万的数据也同样进行拆分,到最后设置一个阈值来规定当数据规模到达多少时,停止这样分割数据,比如当数据拆分到500条时停止分割,进行递归合并计算
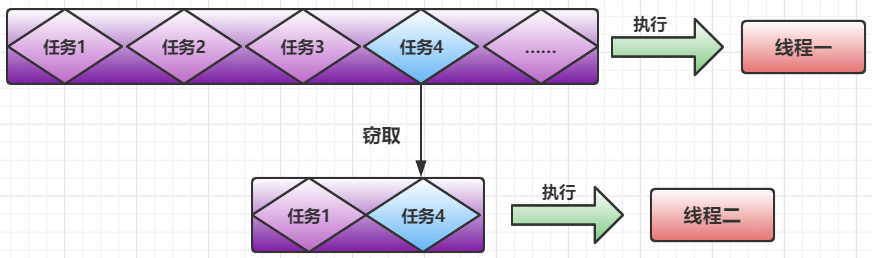
二,任务窃取算法
在任务进行Fork/Join后,每一个子任务会压入不同的线程队列进行执行,这样来实现硬件设备的多核利用
工作窃取算法是整个Fork/Join框架的性能优化,假如A线程的任务队列执行快,B线程的任务队列执行慢,那么在A线程执行完之后,A会窃取B线程任务队列中的任务进行执行
窃取算法的优缺点:
- 优点:充分利用线程进行并行计算,并减少竞争
- 缺点:在某些情况下窃取任务线程和被窃取任务线程存在竞争
窃取任务线程和被窃取任务线程的竞争在Fork/Join框架中做了避免,它采用双端队列存储任务,被窃取任务线程从双端队列的头部拿任务,窃取任务线程从队尾拿线程
三,Fork/Join演示
需求:使用Fork/Join框架计算1-10000的累加,当一个任务的计算数量大于3000时拆分任务,数量小于3000时计算
public class StreamEndMain1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ForkJoinPool fork = new ForkJoinPool();
SumReduceTask sum = new SumReduceTask(1L,10000L);
long s = fork.invoke(sum);
System.out.println(s);
}
}
class SumReduceTask extends RecursiveTask<Long> {
//需要拆分的临界值
private static final long THRESHOLD = 1000L;
//起始值
final private long start;
//终止值
final private long end;
public SumReduceTask(long start,long end) {
this.start=start;
this.end=end;
}
@Override
protected Long compute() {
long len = end - start;
//计算
if(len < THRESHOLD) {
//最终结果
long sum = 0;
for(long a=start;a<end;a++) {
sum+=a;
}
return sum;
}else {//拆分
long middle = (start+end)/2;
SumReduceTask sumreduce1 = new SumReduceTask(start, middle);
sumreduce1.fork();
SumReduceTask sumreduce2 = new SumReduceTask(middle+1, end);
sumreduce2.fork();
return sumreduce1.join()+sumreduce2.join();
}
}
}






Comments | 2 条评论
Warning: Undefined variable $m in /www/wwwroot/wql_luoqin_ltd/wp-content/themes/Sakura/functions.php on line 1767
Warning: Trying to access array offset on value of type null in /www/wwwroot/wql_luoqin_ltd/wp-content/themes/Sakura/functions.php on line 1767
Deprecated: stripslashes(): Passing null to parameter #1 ($string) of type string is deprecated in /www/wwwroot/wql_luoqin_ltd/wp-content/themes/Sakura/functions.php on line 1767
Warning: Undefined variable $m in /www/wwwroot/wql_luoqin_ltd/wp-content/themes/Sakura/functions.php on line 1767
Warning: Trying to access array offset on value of type null in /www/wwwroot/wql_luoqin_ltd/wp-content/themes/Sakura/functions.php on line 1767
Deprecated: stripslashes(): Passing null to parameter #1 ($string) of type string is deprecated in /www/wwwroot/wql_luoqin_ltd/wp-content/themes/Sakura/functions.php on line 1767
itfhghh
@X. vvvv