1. 自定义登录页面
SpringSecurity默认会自动生成一个登录页面(/login),并使用默认URL处理登录的提交内容,登录后跳转到默认URL等。尽管SpringSecurity提供默认登录页面但在真实开发环境中不会使用默认页面,需要自己指定页面
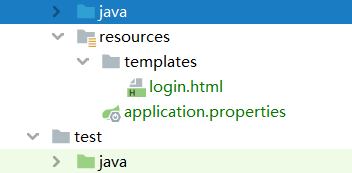
1.1 认证页面准备
认证页面使用Thmeleaf模板
① thymeleaf的maven依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>
② 结构:
③ login.jsp:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" class="no-js">
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
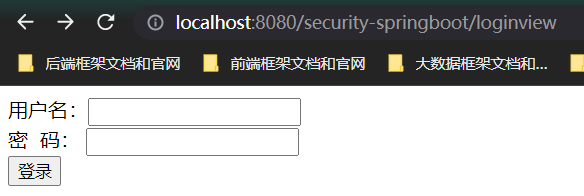
<form action="/security-springboot/login" method="post">
用户名:<input type="text" name="username">
密 码:
<input type="password" name="password">
<input type="submit" value="登录">
</form>
</body>
</html>
1.2 配置认证页面
① 在实现了WebMvcConfigurer接口的配置文件中配置认证页面地址:
@Configuration
public class WebConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
//默认URL根据跳转到/login,此url为spring security提供
@Override
public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) {
//输入项目地址自动重定向到登录页面
registry.addViewController("/").setViewName("redirect:/loginview");
//URL绑定登录页面
registry.addViewController("/loginview").setViewName("/login");
}
}
② 在WebSecurityConfig中配置表单登录信息
@Configuration
public class WebSecurityContext extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
//3,安全拦截机制
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeRequests()
.formLogin()//允许表单登录
.loginPage("/loginview")//指定自定义登录页,security以重定向方式跳转到/login-view
.loginProcessingUrl("/login")//指定登录处理URL,也就是用户名、密码表单提交的目的路径
.successForwardUrl("/login-success")//自定义登录成功的跳转页面地址
.permitAll();//允许任何用户访问表单登录页
}
}
- formLogin():允许表单登录
- loginPage():指定自定义登录页,security以重定向方式跳转到指定页面
- loginProcessingUrl():指定登录处理URL,也就是用户名、密码表单提交的目的路径
- successForwardUrl():自定义登录成功的跳转页面地址
- permitAll():允许任何用户访问表单登录页
测试:
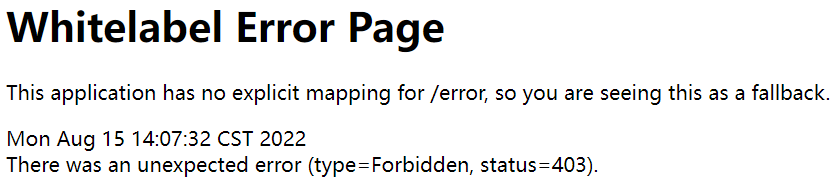
1.3 解决错误
问题出现的原因:SpringSecurity为防止CSRF(Cross-site request forgerf跨站请求伪造)的发生,限制了除get以外的大多数方法
1)解决方案1:屏蔽CSRF控制,即SpringSecurity不再限制CSRF
配置WebSecurityConfig
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.csrf().disable();//屏蔽CSRF控制
}
2)解决方案2:再页面请求时添加一个Token,SpringSecurity会验证token,如果token合法则可以继续请求
<form action="/security-springboot/login" method="post">
<input type="hidden" name="${_csrf.parameterName} value="${_csrf.token}">
</form>
2. 连接数据库认证
在案例中都是将用户信息使用硬编码的方式存储在内存中,实际项目中用户信息存储在数据库中,这次从数据库读取用户信息进行认证
2.1 创建数据表
表的SQL:
CREATE TABLE `security_user`( `id` bigint(20) NOT NULL COMMENT '用户id', `username` VARCHAR(64) NOT NULL, `password` VARCHAR(64) NOT NULL, `fullname` VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL, `mobile` VARCHAR(11) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT "手机号", PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE )
2.2 数据库模块
① 导入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.21</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbc</artifactId>
</dependency>
② application.properties配置
spring.datasource.driver-class-name= com.mysql.jdbc.Driver spring.datasource.url= jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springcloud_test?serverTimezone=UTC&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8 spring.datasource.username= root spring.datasource.password= 123
③ 定义pojo
@Data
public class SecurityUserDao {
private int id;
private String username;
private String password;
private String fullname;
private String mobile;
}
④ 定义Dao
@Repository
public class userDao {
@Autowired
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
//根据用户名查询用户信息
public SecurityUserDao getUserByUserName(String username){
String SQL = "SELECT id,username,password,fullname,mobile FROM security_user WHERE username=?";
List<SecurityUserDao> query = jdbcTemplate.query(SQL, new Object[]{username}, new BeanPropertyRowMapper<SecurityUserDao>(SecurityUserDao.class));
if(query!=null && query.size()==1){
return query.get(0);
}
return null;
}}
2.3 权限模块
① SpringSecurity的配置
@Configuration
public class WebSecurityContext extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
//2,密码编码器
@Bean
public PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder(){
//不需要对密码进行编码
return NoOpPasswordEncoder.getInstance();
}
//3,安全拦截机制
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/wql/**").authenticated()//所有/wql/**的请求必须认证通过
.anyRequest().permitAll()//除了/wql/))其他请求可以访问
.and()
.formLogin()//允许表单登录
.loginPage("/loginview")
.loginProcessingUrl("/login")
.successForwardUrl("/login-success")//自定义登录成功的页面地址
.failureForwardUrl("/login-failure")
.permitAll();
http.csrf().disable();
}
}
@Service
public class SpringDataUserDetailsService implements UserDetailsService {
@Autowired
userDao userDao;
@Override
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String s) throws UsernameNotFoundException {
//1.将来连接数据库根据账号查询用户信息
SecurityUserDao userByUserName = userDao.getUserByUserName(s);
if(userByUserName==null){
return null;
}
//2.登录账号
UserDetails build = User.withUsername(userByUserName.getUsername()).password(userByUserName.getPassword()).authorities("a1").build();
return build;
}
}
3. 连接数据库授权
3.1 数据库准备
① 用户表
CREATE TABLE `security_user`( `id` bigint(20) NOT NULL COMMENT '用户id', `username` VARCHAR(64) NOT NULL, `password` VARCHAR(64) NOT NULL, `fullname` VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL, `mobile` VARCHAR(11) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT "手机号", PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE )
② 角色表
CREATE TABLE `t_role`(
`id` VARCHAR(32) NOT NULL,
`role_name` VARCHAR(255) DEFAULT NULL,
`description` VARCHAR(255) DEFAULT NULL,
`create_time` DATETIME DEFAULT NULL,
`update_time` DATETIME DEFAULT NULL,
`status` char(1) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY(`id`)
)ENGINE=INNODB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8
③ 用户角色关系表
CREATE TABLE `t_user_role`(
`user_id` VARCHAR(32) NOT NULL,
`role_id` VARCHAR(32) NOT NULL,
`create_time` datetime DEFAULT NULL,
`create` VARCHAR(255) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY(`user_id`,`role_id`)
)ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
④ 权限表
CREATE TABLE `t_permission`(
`id` VARCHAR(32) NOT NULL,
`code` VARCHAR(32) NOT NULL,
`description` VARCHAR(64) DEFAULT NULL,
`url` VARCHAR(128) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY(`id`)
)ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
⑤ 角色权限关系表
CREATE TABLE `t_role_permission`(
role_id VARCHAR(32) NOT NULL,
permission_id VARCHAR(32) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY(role_id,permission_id)
)ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
查询SQL:通过userid查权限
SELECT * FROM t_permission WHERE id IN(
SELECT role_id FROM t_role_permission WHERE role_id IN(
SELECT role_id FROM t_user_role WHERE user_id =?
))
3.2 授权代码
① POJO
@Data
public class PessmissionPojo {//权限表
String id;
String code;
String description;
String url;
}
② Dao
@Repository
public class userDao {
@Autowired
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
//根据用户ID查询用户权限
public List<String> findPermissionByUserID(String userid){
String SQL = "SELECT * FROM t_permission WHERE id IN(\n"+
"SELECT role_id FROM t_role_permission WHERE role_id IN(\n"+
"SELECT role_id FROM t_user_role WHERE user_id =?\n"+"))";
List<PessmissionPojo> query = jdbcTemplate.query(SQL, new Object[]{userid}, new BeanPropertyRowMapper<PessmissionPojo>(PessmissionPojo.class));
ArrayList<String> permission = new ArrayList<>();
query.forEach((x)->permission.add(x.getCode());
return permission;
}
}
③ 自定义安全拦截
@Service
public class SpringDataUserDetailsService implements UserDetailsService {
@Autowired
userDao userDao;
@Override
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String s) throws UsernameNotFoundException {
//1.将来连接数据库根据账号查询用户信息
SecurityUserPojo userByUserName = userDao.getUserByUserName(s);
if(userByUserName==null){
return null;
}
//2. 通过用户ID查询权限
List<String> permissionByUserID = userDao.findPermissionByUserID(new StringBuffer().append(userByUserName.getId()));
//3. 将permissionByUserID转化成数组
String[] permissions = new String[permissionByUserID.size()];
permissionByUserID.toArray(permissions);
//2.登录账号
UserDetails build = User.withUsername(userByUserName.getUsername()).password(userByUserName.getPassword()).authorities(permissions).build();
return build;
}
}
④ Security配置
@Configuration
public class WebSecurityContext extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
//2,密码编码器
@Bean
public PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder(){
//不需要对密码进行编码
return NoOpPasswordEncoder.getInstance();
}
//3,安全拦截机制
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/wql/a1").hasAuthority("p1")//所有/wql/**的请求必须认证通过
.anyRequest().permitAll()//除了/wql/))其他请求可以访问
.and()
.formLogin()//允许表单登录
.loginPage("/loginview")
.loginProcessingUrl("/login")
.successForwardUrl("/login-success")//自定义登录成功的页面地址
.failureForwardUrl("/login-failure")
.permitAll();
http.csrf().disable();
}
}
4. 自定义授权方式
Security授权包括两种:
- web授权:通过url拦截进行授权
- 方法授权:通过方法拦截进行授权
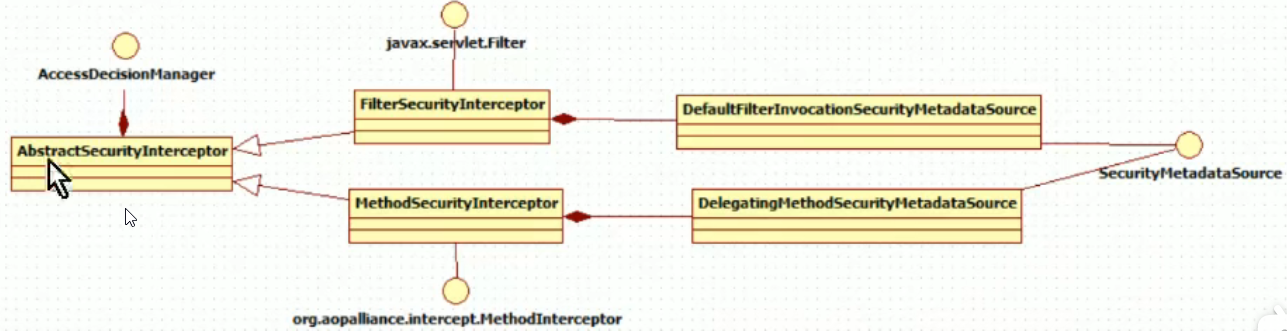
底层它们都会调用accessDecisionManager进行授权决策,若为web授权则拦截器为FilterSecurityInterception,若为方法授权则拦截器为MethodSecurityInterceptor,如果同时通过web授权和方法授权则先执行web授权,在执行方法授权,最后决策通过允许访问资源
类关系如下:
4.1 web授权
Web授权在WebSecurityContext配置文件中的安全拦截方法(configure)中配置
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/wql/a1").hasAuthority("p1")//所有/wql/**的请求必须认证通过
.anyRequest().permitAll()//除了/wql/))其他请求可以访问
}
- anyRequest():表示任意请求
- authenticated():保护URL,需要用户登录
- permitAll():指定URL无需保护,一般应用与静态资源文件
- hasRole(String role):限制单个角色访问,角色将被增加"ROLE_"所以"ADMIN"将和"ROLE_ADMIN"进行比较
- hasAuthority(String authority):限制单个权限访问
- hasAnyRole(String……roles):允许多个角色访问
- hasAnyAuthority(String……authorities):允许多个权限访问
- access(String attribute):该方法使用SpEL表达式,可以创建复杂的限制
- haslpAddress(String ipadressExpression):限制IP地址或子网
注:权限的规则的顺序也是非常重要的,更具体的规则应该先写,因为前的规则会覆盖后面的规则,所以在编写权限时需要由小及大
例:权限无效
http.authorizeRequests()
.anyRequest().permitAll()
.antMatchers("/wql/a1").hasAuthority("p1")
后的"/wql/a1"访问权限p1会被覆盖掉,应该anyRequest().permitAll()允许所有请求
web授权尽量使用基于资源的授权,减少基于角色的授权
4.2 方法授权
从SpringSecurity2.0开始,它支持服务层方法的安全性支持,方法授权是在Controller方法层面进行授权,通过注解的方式
方法授权的三类注解:
- @PreAuthorize
- @PostAuthorize
- @Secured
4.2.1 @Secured
需要在任意@Configuration实例上使用@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity注释来启用基于注解的安全性,以下内容启用SpringSecurity的@Secured注释
@Configuration
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(securedEnabled = true)
public class WebSecurityContext extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
………………
}
例:
@GetMapping("/helloUser")
@Secured({"ROLE_normal","ROLE_admin"})
public String helloUser() {
return "hello,user";
}
拥有normal或者admin角色的用户都可以方法helloUser()方法。另外需要注意的是这里匹配的字符串需要添加前缀“ROLE_“
假如要设置同时拥有admin & noremal的用户才能方法helloUser()方法,这时候@Secured就无能为力了,需要其他两个注解来完成
4.2.2 @PreAuthorize
Spring的 @PreAuthorize/@PostAuthorize 注解更适合方法级的安全,也支持Spring SpEL表达式语言,提供了基于表达式的访问控制
当@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled=true)的时候,@PreAuthorize可以使用:
@Configuration
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled= true)
public class WebSecurityContext extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
………………
}
例:拥有normal或者admin角色的用户都可以方法helloUser()方法,此时如果我们要求用户必须同时拥有normal和admin的话,那么可以这么编码
@GetMapping("/helloUser")
@PreAuthorize("hasRole('normal') AND hasRole('admin')")
public String helloUser() {
return "hello,user";
}
4.2.3 @PostAuthorize
@PostAuthorize 注解使用并不多,在方法执行后再进行权限验证,适合验证带有返回值的权限,Spring EL 提供 返回对象能够在表达式语言中获取返回的对象returnObject
当@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled=true)的时候,@PostAuthorize可以使用:
@Configuration
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled= true)
public class WebSecurityContext extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
………………
}
例:
@GetMapping("/helloUser")
@PostAuthorize(" returnObject!=null && returnObject.username == authentication.name") public User helloUser() {
Object pricipal = SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication().getPrincipal();
User user;
if("anonymousUser".equals(pricipal)) {
user = null;
}else {
user = (User) pricipal;
}
return user;
}
注: 这三个最常用也就是@PreAuthorize这个注解了,在使用中主要是配合Spring EL表达式。
5. 会话管理
用户认证通过后,为了避免用户的每次操作都进行认证可将用户的信息保存在会话中。SpringSecurity提供会话管理,认证通过后将身份信息存入SecurityContextHolder上下文,SecurityContext与当前线程进行绑定,方便获取用户身份
5.1 获取会话信息
编写LoginController,实现/wql/a1和/wql/a2的测试资源,并修改success和failure方法
@RestController
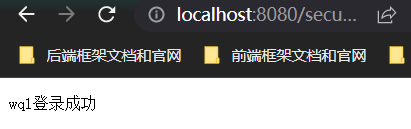
public class logincontroller {
@RequestMapping(value = "/login-success", produces = "text/plain;charset=UTF-8")
public String success() {
String username =getUsername();
return username+"登录成功";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/login-failure", produces = "text/plain;charset=UTF-8")
public String failure() {
String username =getUsername();
return username+"登录失败";
}
//获取用户名
private String getUsername() {
//用户名
String username = null;
//通过SecurityContextHolder获取认证通过的用户信息Authentication
Authentication authentication = SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication();
//通过Authentication的用户身份信息
Object principal = authentication.getPrincipal();
if (principal == null) {
username = "匿名用户";
}
//判断principal是否是UserDetails的子类
if (principal instanceof UserDetails) {
//强转
UserDetails userDetails = (UserDetails) principal;
//获取username
username = userDetails.getUsername();
}
return username;
}
}
通过SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication()获取Authentication,而Authentication就保存权限信息、细节信息、身份信息等
测试:





Comments | NOTHING