1. EasyExcel的介绍
EasyExcel是由阿里开源的excel解析读取写入框架,生成Excel比较有名的框架有Apache poi、jxl。但他们都存在一个严重的问题就是非常的耗内存,poi有一套SAX模式的API可以一定程度的解决一些内存溢出的问题,但POI还是有一些缺陷,比如07版Excel解压缩以及解压后存储都是在内存中完成的,内存消耗依然很大。easyexcel重写了poi对07版Excel的解析,一个3M的excel用POI sax解析依然需要100M左右内存,改用easyexcel可以降低到几M,并且再大的excel也不会出现内存溢出;03版依赖POI的sax模式,在上层做了模型转换的封装,让使用者更加简单方便
官方网站:
- 官方网站:https://easyexcel.opensource.alibaba.com/
- github地址:https://github.com/alibaba/easyexcel
- gitee地址:https://gitee.com/easyexcel/easyexcel
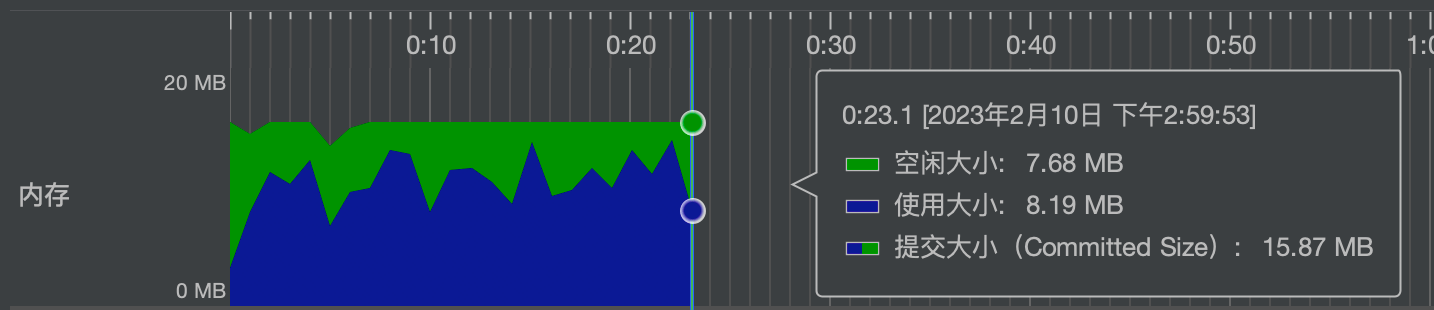
16M内存23秒读取75M(46W行25列)的Excel(3.2.1+版本):
总结:EasyExcel是快速、简单、避免OOM的java处理Excel工具
注意:这个工具操作方法官方文档提供的非常详细,甚至连需求如何写的代码都有对应案例
2. EasyExcel写操作
2.1 写操作基本使用
引入依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>easyexcel</artifactId>
<version>3.1.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>1.18.12</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
使用步骤:
- 新建Excel模板类
- 通过工具操作类进行读写操作
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@ToString
@Data
@EqualsAndHashCode
public class exceluserpojo {
@ExcelProperty("用户编号")
private Integer userId;
@ExcelProperty("姓名")
private String userName;
@ExcelProperty("性别")
private String gender;
@ExcelProperty("工资")
private Double salary;
@ExcelProperty("入职时间")
private Date hireDate;
}
- @ExcelProperty:这个注解的作用是描述设置Excel表格的头名称
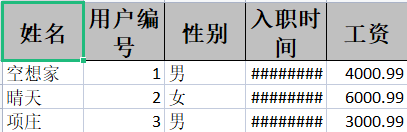
② 写法一:使用链式调用写法
@Test
public void test01(){
//创建Excel文档
String fileName = "user1.xlsx";
//根据exceluserpojo模板构建数据
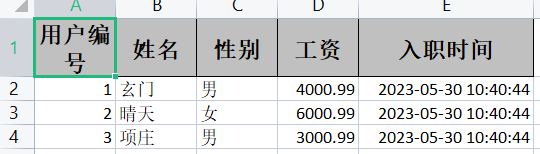
List<exceluserpojo> exceluserpojos = new ArrayList<exceluserpojo>();
exceluserpojos.add(new exceluserpojo(1,"空想家","男",4000.99,new Date()));
exceluserpojos.add(new exceluserpojo(2,"晴天","女",6000.99,new Date()));
exceluserpojos.add(new exceluserpojo(3,"项庄","男",3000.99,new Date()));
//向Excel表格中写数据
EasyExcel.write(fileName,exceluserpojo.class).sheet("用户信息表").doWrite(exceluserpojos);
}
- write():文件写入的位置和对应模板类
- sheet():表对象设置,有参为表名称
- doWrite():具体写入什么数据,传入Collection的子类
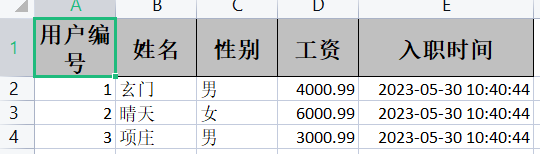
③ 写法二:使用普通的对象写法
@Test
public void test02(){
//创建Excel文档
String fileName = "user1.xlsx";
//根据exceluserpojo模板构建数据
List<exceluserpojo> exceluserpojos = new ArrayList<exceluserpojo>();
exceluserpojos.add(new exceluserpojo(1,"玄门","男",4000.99,new Date()));
exceluserpojos.add(new exceluserpojo(2,"晴天","女",6000.99,new Date()));
exceluserpojos.add(new exceluserpojo(3,"项庄","男",3000.99,new Date()));
//获取ExcelWriterBuilder对象
ExcelWriter execlWrite = EasyExcel.write(fileName, exceluserpojo.class).build();
//创建sheet对象
WriteSheet sheet = EasyExcel.writerSheet("用户信息").build();
//将数据写入sheet标签中
execlWrite.write(exceluserpojos,sheet);
//关闭流,文件流手动关闭
execlWrite.finish();
}
2.2 写操作高级使用
高级写法有:
- 排除某些字段写入
- 只允许某些字段写入
- 设置excel表格中列的顺序
- 复杂头写入
- 写入不同的sheet中
- 日期数字格式化
- 将图片写入excel
2.2.1 排除字段写入
步骤:
- 创建需要排除的属性集合,将表头名称传入
- 调用EasyExcel的excludeColumnFieldNames()方法排除对应的属性
演示:
//排除字段写入
@Test
public void test03(){
//创建Excel文档
String fileName = "excludeuser.xlsx";
//根据exceluserpojo模板构建数据
List<exceluserpojo> exceluserpojos = new ArrayList<exceluserpojo>();
exceluserpojos.add(new exceluserpojo(1,"空想家","男",4000.99,new Date()));
exceluserpojos.add(new exceluserpojo(2,"晴天","女",6000.99,new Date()));
exceluserpojos.add(new exceluserpojo(3,"项庄","男",3000.99,new Date()));
//设置排除的属性集合
Set<String> set = new HashSet<>();
set.add("salary");
set.add("gender");
//向Excel表格中写数据
EasyExcel.write(fileName,exceluserpojo.class)
//排除属性
.excludeColumnFieldNames(set)
.sheet("用户信息表")
.doWrite(exceluserpojos);
}
2.2.2 允许字段写入
步骤和排除字段写入相似:
- 创建需要写入的属性集合,将表头名称传入
- 调用EasyExcel的includeColumnFieldNames()方法排除对应的属性
//只允许字段写入
@Test
public void test04(){
//创建Excel文档
String fileName = "includeuser.xlsx";
//根据exceluserpojo模板构建数据
List<exceluserpojo> exceluserpojos = new ArrayList<exceluserpojo>();
exceluserpojos.add(new exceluserpojo(1,"空想家","男",4000.99,new Date()));
exceluserpojos.add(new exceluserpojo(2,"晴天","女",6000.99,new Date()));
exceluserpojos.add(new exceluserpojo(3,"项庄","男",3000.99,new Date()));
//设置排除的属性集合
Set<String> set = new HashSet<>();
set.add("userName");
set.add("gender");
//向Excel表格中写数据
EasyExcel.write(fileName,exceluserpojo.class)
//只包含属性
.includeColumnFieldNames(set)
.sheet("用户信息表")
.doWrite(exceluserpojos);
}
2.2.3 设置列的顺序
列的顺序设置通过模板类的@ExcelProperty中的index设置优先级
例:
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@ToString
@Data
@EqualsAndHashCode
public class exceluserpojo {
@ExcelProperty(value = "用户编号",index = 1)
private Integer userId;
@ExcelProperty(value = "姓名",index = 0)
private String userName;
@ExcelProperty(value = "性别",index = 2)
private String gender;
@ExcelProperty(value = "工资",index = 4)
private Double salary;
@ExcelProperty(value = "入职时间",index = 3)
private Date hireDate;
}
写出测试:
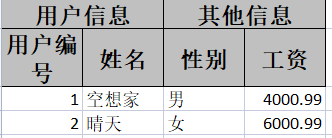
2.2.4 复杂头写入
复杂头指的是多级表头,复杂头的设置在@ExcelProperty的value属性,value通过{}包含多个表头,第一个值为后面值的父表头
例:
@NoArgsConstructor
@ToString
@Data
@EqualsAndHashCode
public class themeuserpojo {
@ExcelProperty(value = {"用户信息","用户编号"})
private Integer userId;
@ExcelProperty(value = {"用户信息","姓名"})
private String userName;
@ExcelProperty(value = {"其他信息","性别"})
private String gender;
@ExcelProperty(value = {"其他信息","工资"})
private Double salary;
}
2.2.5 写入不同的sheet中
写不同的sheet需要使用对象式的写法,将sheet提取出来进行批量不同写入
例:
@Test//写入不同的sheet
public void test07(){
//创建Excel文档
String fileName = "diffsheet.xlsx";
//根据exceluserpojo模板构建数据
List<exceluserpojo> exceluserpojos = new ArrayList<exceluserpojo>();
exceluserpojos.add(new exceluserpojo(1,"空想家","男",4000.99,new Date()));
exceluserpojos.add(new exceluserpojo(2,"晴天","女",6000.99,new Date()));
//获取ExcelWriter对象
ExcelWriter excelWriter = EasyExcel.write(fileName, exceluserpojo.class).build();
for(int i=0;i<4;i++){
WriteSheet build = EasyExcel.writerSheet("用户表" + i).build();
excelWriter.write(exceluserpojos,build);
}
excelWriter.finish();
}
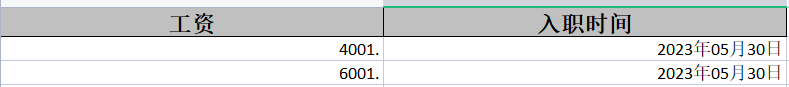
2.2.6 日期数字格式化
格式化涉及到两个注解:
- @NumberFormat:数字格式化(使用#为占位符)
- @DateTimeFormat:日期格式化(yyyy MM dd等格式)
例:
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@ToString
@Data
@EqualsAndHashCode
public class dataformatpojo {
@NumberFormat("#.##")
@ExcelProperty(value = "工资")
private Double salary;
@DateTimeFormat("yyyy年MM月dd日")
@ExcelProperty(value = "入职时间")
private Date hireDate;
}
2.2.7 将图片写入excel
将文件写入excel可以使用多种对象方式:
- 抽象文件类表示(File)
- 输入流表示(InputStream)
- String表示
- 二进制数据保存一张图片
- url保存一张图片
例:
① 模板类
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@ToString
@Data
public class ImageData {
//使用抽象文件表示一个图片
private File file;
//使用输入流保存一个文件
private InputStream inputStream;
//使用String类型表示保存一个图片,需要使用StringImageConverter转换器
@ExcelProperty(converter = StringImageConverter.class)
private String imgStr;
//使用二进制数据保存为一种图片
private byte[] byteArray;
//使用网络链接保存一个图片
private URL url;
}
② 写入操作
@Test
public void test() throws IOException {
String name = "imageuser.xlsx";
ArrayList<ImageData> arrayList = new ArrayList<>();
ImageData imageData = new ImageData();
imageData.setFile(new File("wql.jpg"));
imageData.setInputStream(new FileInputStream(new File("wql.jpg")));
imageData.setImgStr("wql.jpg");
imageData.setUrl(new URL("https://wql.luoqin.ltd/wp-content/uploads/2022/06/1-2.jpg"));
byte[] b = new byte[(int)new File("wql.jpg").length()];
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("wql.jpg");
fileInputStream.read(b,0,(int)new File("wql.jpg").length());
imageData.setByteArray(b);
//添加到集合
arrayList.add(imageData);
EasyExcel.write(name,ImageData.class).sheet("图片写入表").doWrite(arrayList);
}
3. EasyExcel读操作
3.1 简单读操作
简单读操作两种写法:
- 链式调用写法
- 对象式写法
和写一样读操作需要指定需要读的文件地址、接收的模板对象(如果xslx一样写入模板可以和读取模板一样),最后最重要的是使用AnalysisEventListener回调函数(可以单独声明也可以使用匿名内部类)
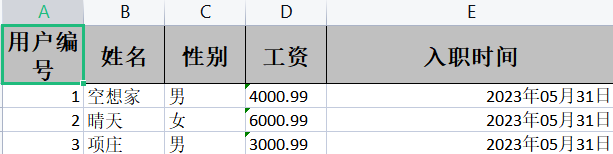
读入的xslx:
接收的模板对象:和写模板一样
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@ToString
@Data
public class exceluserpojo {
private Integer userId;
private String userName;
private String gender;
private Double salary;
private Date hireDate;
}
例:
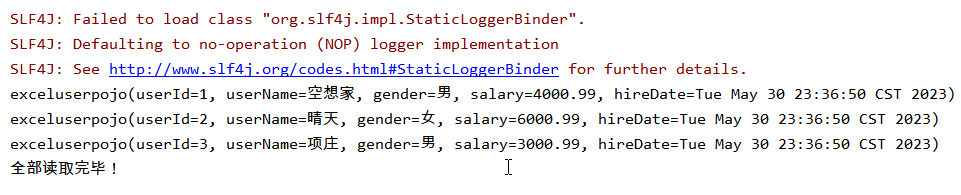
① 第一种写法:链式调用,最后需要指定sheet并提供doread触发读取
@Test
public void easyreadtest() throws IOException {
String filepathname = "G:\\Java-Dome\\EasyExcel-Dome\\user1.xlsx";
EasyExcel.read("G:\\Java-Dome\\EasyExcel-Dome\\user1.xlsx", exceluserpojo.class, new AnalysisEventListener<exceluserpojo>() {
@Override
public void invoke(exceluserpojo o, AnalysisContext analysisContext) {
System.out.println(o);
}
@Override
public void doAfterAllAnalysed(AnalysisContext analysisContext) {
}
}).sheet().doRead();
}
② 第二种写法:对象调用
@Test
public void easyreadtest2() throws IOException {
String filepathname = "G:\\Java-Dome\\EasyExcel-Dome\\user1.xlsx";
ExcelReader excelReader = EasyExcel.read("G:\\Java-Dome\\EasyExcel-Dome\\user1.xlsx", exceluserpojo.class, new AnalysisEventListener<exceluserpojo>() {
@Override
public void invoke(exceluserpojo o, AnalysisContext analysisContext) {
System.out.println(o);
}
@Override
public void doAfterAllAnalysed(AnalysisContext analysisContext) {
System.out.println("全部读取完毕!");
}
}).build();
//创建sheet对象,并读取excel的第1个sheet(下标从0开始)
ReadSheet sheet = EasyExcel.readSheet(0).build();
excelReader.read(sheet);
//关闭流操作,在读取文件时会创建临时文件,如果不关闭,磁盘会爆掉
excelReader.finish();
}
3.2 高级读操作
高级读操作有:
- 通过列名称或者下标获取指定列
- 读取数据进行格式化
- 读取全部的sheet表格
- 读取指定sheet表格
3.2.1 读取指定列
读取指定列指的是将对应列读取到对应模板类的属性中,这个也是借助@ExcelProperty它不仅可以在写中使用在读取中也需要通过它进行匹配性的读入
指定列读取:
- @ExcelProperty(value=""):通过名称读入指定列到指定类属性
- @ExcelProperty(index=""):通过下标读入指定列到指定类属性
读入的xslx:
模板:
@EqualsAndHashCode
@Data
public class exceluserpojo {
@ExcelProperty(value = "用户编号")
private Integer userId;
@ExcelProperty(value = "姓名")
private String userName;
@ExcelProperty(value = "性别")
private String gender;
@ExcelProperty(value = "工资")
private Double salary;
@ExcelProperty(value = "入职时间")
private Date hireDate;
}
例:
@Test
public void easyreadtest() throws IOException {
String filepathname = "G:\\Java-Dome\\EasyExcel-Dome\\user1.xlsx";
EasyExcel.read("G:\\Java-Dome\\EasyExcel-Dome\\user1.xlsx", exceluserpojo.class, new AnalysisEventListener<exceluserpojo>() {
@Override
public void invoke(exceluserpojo o, AnalysisContext analysisContext) {
System.out.println(o);
}
@Override
public void doAfterAllAnalysed(AnalysisContext analysisContext) {
System.out.println("全部读取完毕!");
}
}).sheet().doRead();
}
3.2.2 读取格式化数据
读取格式化数据也依赖EasyExcel的@NumberFormat和@DateTimeFormat注解,当读取的excel内容数据是格式化的时,通过这个两个注解去匹配格式化数据进行读取不然读取时就会报错
注:当格式化读取数值类型时@NumberFormat失效,建议将类型换成String在读取后再转换成Double,不建议总结使用Double
读取数据内容格式:
读取模板:
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@ToString
@Data
@EqualsAndHashCode
public class exceluserpojo {
@ExcelProperty(value = "用户编号")
private Integer userId;
@ExcelProperty(value = "姓名")
private String userName;
@ExcelProperty(value = "性别")
private String gender;
@ExcelProperty(value = "工资")
@NumberFormat("#.##")
private String salary;
@ExcelProperty(value = "入职时间")
@DateTimeFormat("yyyy年MM月dd日")
private Date hireDate;
}
例:
@Test
public void easyreadtest() throws IOException {
String filepathname = "G:\\Java-Dome\\EasyExcel-Dome\\user1.xlsx";
EasyExcel.read("G:\\Java-Dome\\EasyExcel-Dome\\user1.xlsx", exceluserpojo.class, new AnalysisEventListener<exceluserpojo>() {
@Override
public void invoke(exceluserpojo o, AnalysisContext analysisContext) {
System.out.println(o);
}
@Override
public void doAfterAllAnalysed(AnalysisContext analysisContext) {
System.out.println("全部读取完毕!");
}
}).sheet().doRead();
}
3.2.3 读取全部sheet表格
读取全部的sheet表格不需要指定sheet表格,但需要注意的是要保证所有的sheet使用的模板是一样的,不然如果某一个模板不匹配就会报错
- 全部读取是使用doReadAll()方法
读取的多个sheet数据:
模板:和读取格式化数据模板一样
例:每结束读取一个sheet会触发一次doAfterAllAnalysed()方法
@Test
public void Allreadtest() throws IOException {
String filepathname = "G:\\Java-Dome\\EasyExcel-Dome\\user1.xlsx";
EasyExcel.read("G:\\Java-Dome\\EasyExcel-Dome\\user1.xlsx", exceluserpojo.class, new AnalysisEventListener<exceluserpojo>() {
@Override
public void invoke(exceluserpojo o, AnalysisContext analysisContext) {
System.out.println(o);
}
@Override
public void doAfterAllAnalysed(AnalysisContext analysisContext) {
System.out.println("全部读取完毕!");
}
}).doReadAll();
}
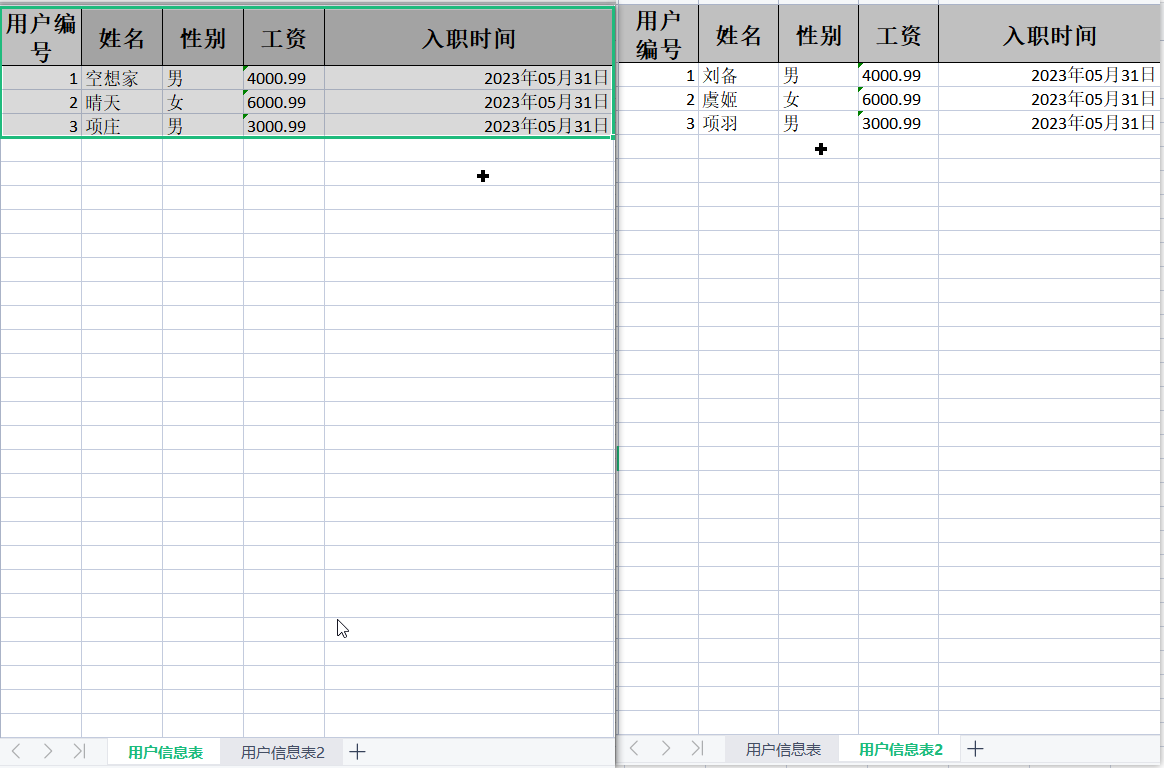
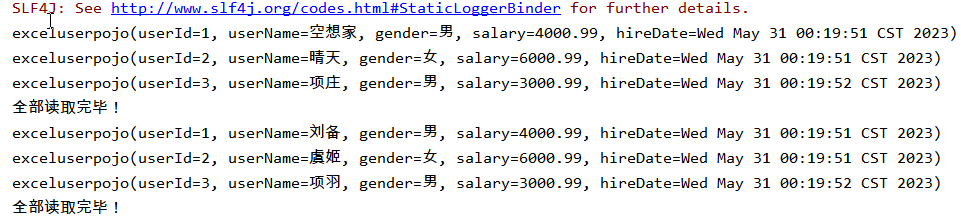
3.2.4 读取指定sheet表格
读取指定的sheet表格,可能每一个sheet数据模板不一样需要单独指定模板,EasyExcel提供了方便只需要创建一次ExcelReader对象,手动指定sheet和模板
指定读取sheet数据:
模板对象:
① exceluserpojo
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@ToString
@Data
@EqualsAndHashCode
public class exceluserpojo {
@ExcelProperty(value = "用户编号")
private Integer userId;
@ExcelProperty(value = "姓名")
private String userName;
@ExcelProperty(value = "性别")
private String gender;
@ExcelProperty(value = "工资")
@NumberFormat("#.##")
private String salary;
@ExcelProperty(value = "入职时间")
@DateTimeFormat("yyyy年MM月dd日")
private Date hireDate;
}
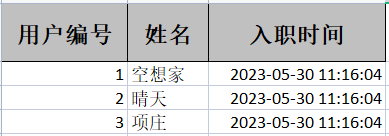
② excludepojo
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@ToString
@Data
@EqualsAndHashCode
public class excludepojo {
@ExcelProperty(value = "用户编号")
private Integer userId;
@ExcelProperty(value = "姓名")
private String userName;
@ExcelProperty(value = "性别")
private String gender;
}
例:
@Test
public void zhidreadtest() throws IOException {
String filepathname = "G:\\Java-Dome\\EasyExcel-Dome\\user1.xlsx";
ExcelReader excelReader = EasyExcel.read(filepathname).build();
//读取第一个sheet
ReadSheet readSheet1 = EasyExcel.readSheet(0).head(exceluserpojo.class).registerReadListener(new AnalysisEventListener<exceluserpojo>() {
@Override
public void invoke(exceluserpojo o, AnalysisContext analysisContext) {
System.out.println(o);
}
@Override
public void doAfterAllAnalysed(AnalysisContext analysisContext) {
System.out.println("sheet1全部读取完毕!");
}
}).build();
//读取第二个sheet
ReadSheet readSheet2 = EasyExcel.readSheet(1).head(excludepojo.class).registerReadListener(new AnalysisEventListener<excludepojo>() {
@Override
public void invoke(excludepojo o, AnalysisContext analysisContext) {
System.out.println(o);
}
@Override
public void doAfterAllAnalysed(AnalysisContext analysisContext) {
System.out.println("sheet2全部读取完毕!");
}
}).build();
//批量读取两个sheet
excelReader.read(readSheet1,readSheet2);
//关闭流
excelReader.finish();
}
4.EasyExcel其他操作
4.1 样式设置
EasyExcel写入时的样式设置包括:
- 列宽、行高、内容高度设置
- 头背景、头字体设置
- 内容背景、内容字体设置
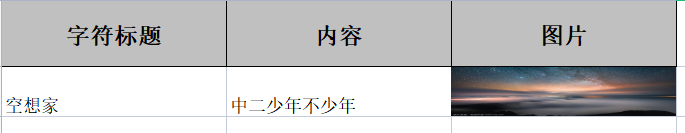
4.1.1 列宽行高设置
列宽行高内容高度涉及到三个注解:
- @ContentRowHeight():设置内容高度
- @HeadRowHeight():设置标题高度
- @ColumnWidth():设置列宽
这些注解可标记在类上也可以标记的在属性上,标记在类上的注解可以控制属性的行高,标记在属性上的注解可以覆盖类上的控制
例:
① 模板类
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@ToString
@Data
@ContentRowHeight(30)//设置内容高度
@HeadRowHeight(40)//设置标题高度
@ColumnWidth(25)//设置列宽
public class WidthAndHeighpojo {
@ExcelProperty(value = "字符标题")
private String title;
@ExcelProperty(value = "内容")
private String content;
@ExcelProperty(value = "图片",converter= StringImageConverter.class)
private String image;
}
② 操作
@DisplayName("列宽行高演示")
public class WidthAndHeighTest {
@Test
public void test() throws IOException {
ArrayList<WidthAndHeighpojo> widthAndHeighpojos = new ArrayList<WidthAndHeighpojo>();
widthAndHeighpojos.add(new WidthAndHeighpojo("空想家","中二少年不少年","wql.jpg"));
EasyExcel.write("WidthAndHeigh.xlsx",WidthAndHeighpojo.class).sheet("列宽行高").doWrite(widthAndHeighpojos);
}
4.1.2 样式设置
excel样式设置包括的注解:
- @HeadStyle:头背景颜色样式
- @HeadFontStyle:头字体样式
- @ContentStyle:内容的背景设置
- @ContentFontStyle:内容字体数字
这些注解可标记在类上也可以标记的在属性上,标记在类上的注解可以控制属性的行高,标记在属性上的注解可以覆盖类上的控制
其中在设置颜色时选择FillPatternTypeEnum.SOLID_FOREGROUND,EasyExcle提供IndexedColors颜色枚举类,在fillForegroundColor属性中输入对应的颜色标记即可
例:
① 模板类
//头背景设置成红色
@HeadStyle(fillPatternType = FillPatternTypeEnum.SOLID_FOREGROUND,fillForegroundColor =10)
//头字体大小设置成20
@HeadFontStyle(fontHeightInPoints = 20)
//设置内容背景颜色为蓝色
@ContentStyle(fillPatternType = FillPatternTypeEnum.SOLID_FOREGROUND,fillForegroundColor =4)
//内容字体设置成20
@ContentFontStyle(fontHeightInPoints = 20)
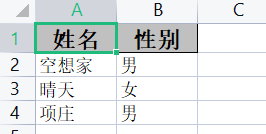
public class stylepojo {
@ExcelProperty(value = "字符标题")
private String title;
@ExcelProperty(value = "内容")
private String content;
}
② 操作
@Test
public void test() throws IOException {
ArrayList<stylepojo> stylepojos = new ArrayList<stylepojo>();
stylepojos.add(new stylepojo("空想家","中二少年不少年"));
EasyExcel.write("WidthAndHeigh.xlsx",stylepojo.class).sheet("样式").doWrite(stylepojos);
}
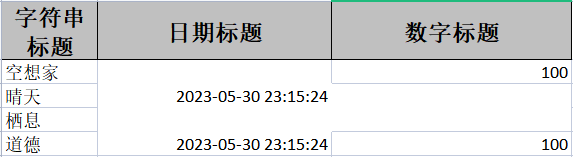
4.2 合并单元格
合并单元格的注解:
- @ContentLoopMerge:每列对行的合并
- @OnceAbsoluteMerge:列的合并,指定从那一行开始,那一行结束,那一列开始,那一列结束,参数如下
- firstRowIndex:起始行的索引,从0开始
- lastRowIndex:结束行索引
- firstColumnIndex:起始列索引
- lastColumnIndex:结束列索引
例:
① 模板类
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@ToString
@Data
//将第2-3行的2-3列合并成一个单元格
@OnceAbsoluteMerge(firstRowIndex = 2,lastRowIndex = 3,firstColumnIndex = 1,lastColumnIndex = 2)
public class mergerowpojo {
@ExcelProperty(value = "字符串标题")
private String str;
//这一列每隔2行合并单元格
@ContentLoopMerge(eachRow = 2)
@ExcelProperty(value = "日期标题")
private Date date;
@ExcelProperty(value = "数字标题")
private Double aDouble;
}
②操作
@DisplayName("合并单元格")
public class mergeTest {
@Test
public void test() throws IOException {
ArrayList<mergerowpojo> mergerowpojo = new ArrayList<mergerowpojo>();
mergerowpojo.add(new mergerowpojo("空想家",new Date(),100.0));
mergerowpojo.add(new mergerowpojo("晴天",new Date(),100.0));
mergerowpojo.add(new mergerowpojo("栖息",new Date(),100.0));
mergerowpojo.add(new mergerowpojo("道德",new Date(),100.0));
EasyExcel.write("mergerow.xlsx",mergerowpojo.class).sheet("样式").doWrite(mergerowpojo);
}
}
4.3 数据填充
EasyExcel数据填充的步骤:
- 创建填充的excel模板
- 创建填充对象类
- 进行填充操作
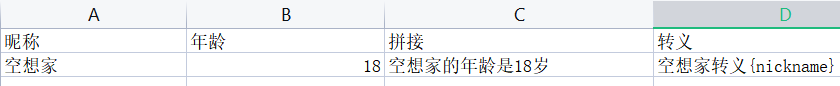
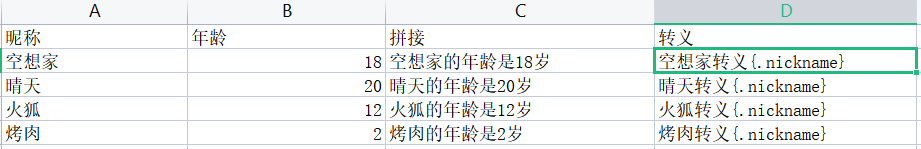
填充模板也是一个Excel,它里面可以写通配占位符:通过{}包裹
- {name}:填充类对象的name属性(单对象填充)
- {.name}:表示填充列表中的所有类中的name属性(多对象填充)
- 如果{}仅仅只表示符号可以通过\进行转义
4.3.1 单对象填充
模板excel:
实体类:
@Data
@ToString
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class fullexcelpojo {
private String nickname;
private Integer age;
}
操作:
@Test
public void dangfulleasttest(){
String exceltempalate = "G:\\Java-Dome\\EasyExcel-Dome\\TemplateExcel.xlsx";
String filepath = "G:\\Java-Dome\\EasyExcel-Dome\\tptoExcel.xlsx";
fullexcelpojo fullexcelpojo = new fullexcelpojo();
fullexcelpojo.setNickname("空想家");
fullexcelpojo.setAge(18);
EasyExcel.write(filepath).withTemplate(exceltempalate).sheet().doFill(fullexcelpojo);
}
-
write:写入的文件路径
-
withTemplate:关联的模板
-
doFill:填充的类对象
4.3.2 多对象填充
模板Excel:
实体类:和单对象时一样
操作:
@Test
public void duofulleasttest(){
String exceltempalate = "G:\\Java-Dome\\EasyExcel-Dome\\TemplateExcel.xlsx";
String filepath = "G:\\Java-Dome\\EasyExcel-Dome\\tptoExcel.xlsx";
ArrayList<fullexcelpojo> arrayList = new ArrayList<>();
arrayList.add(new fullexcelpojo("空想家",18));
arrayList.add(new fullexcelpojo("晴天",20));
arrayList.add(new fullexcelpojo("火狐",12));
arrayList.add(new fullexcelpojo("烤肉",2));
EasyExcel.write(filepath).withTemplate(exceltempalate).sheet().doFill(arrayList);
}
5. EasyExcel文件操作
5.1 文件下载
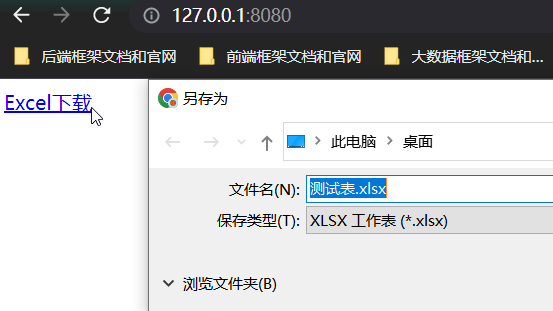
下载过程:
- 构建execl模板对象
- 设置HttpServletResponse的响应信息和头信息
- EasyExcel写操作,输出流使用HttpServletResponse获取流
HttpServletResponse需要做的操作:
- 响应类型和编码
- 下载文件方式(1.附件下载 2.在当前浏览器打开)
- 获取输出流response.getOutputStream()
① 数据模板类
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@ToString
@Data
@EqualsAndHashCode
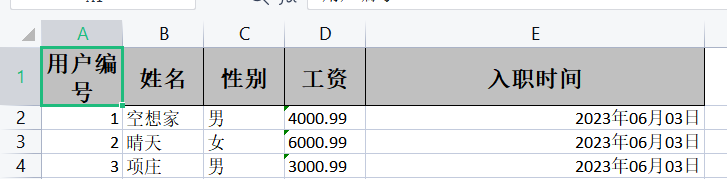
public class exceluserpojo {
@ExcelProperty(value = "用户编号")
private Integer userId;
@ExcelProperty(value = "姓名")
private String userName;
@ExcelProperty(value = "性别")
private String gender;
@ExcelProperty(value = "工资")
@NumberFormat("#.##")
private String salary;
@ExcelProperty(value = "入职时间")
@DateTimeFormat("yyyy年MM月dd日")
private Date hireDate;
}
② 下载实现类
@Controller
public class downloadcontroll {
@RequestMapping("/downloadexcel")
public void downloadexcel(HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {
//设置响应类型和编码
response.setContentType("application/vnd.ms-excel");
response.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
//下载的文件名
String filename = "测试表.xlsx";
//文件名的中文名称编码设置
filename = URLEncoder.encode(filename,"utf-8");
//下载文件方式(1.附件下载 2.在当前浏览器打开)
response.setHeader("Content-dispostion","attachment="+filename+".xlsx");
//根据exceluserpojo模板构建数据
List<exceluserpojo> exceluserpojos = new ArrayList<exceluserpojo>();
exceluserpojos.add(new exceluserpojo(1,"空想家","男","4000.99",new Date()));
exceluserpojos.add(new exceluserpojo(2,"晴天","女","6000.99",new Date()));
exceluserpojos.add(new exceluserpojo(3,"项庄","男","3000.99",new Date()));
//输出流使用HttpServletResponse获取
EasyExcel.write(response.getOutputStream(),exceluserpojo.class).sheet().doWrite(exceluserpojos);
}
}
③ 简单下载网页
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>下载上传页面</title>
</head>
<body>
<a href="http://127.0.0.1:8080/">Excel下载</a>
</body>
</html>
5.2 文件上传
上传过程:
- 导入commons-fileupload文件上传依赖
- 使用MultipartFile接收上传文件
- EasyExcel读取MultipartFile.getInputStream()输入流
- EasyExcel读取数据后的逻辑处理
上传文件:
① 模板对象(和下载一样)
②读取操作
@Controller
public class uploadcontroll {
@RequestMapping(value = "/uploadexcel",method = RequestMethod.POST )
@ResponseBody
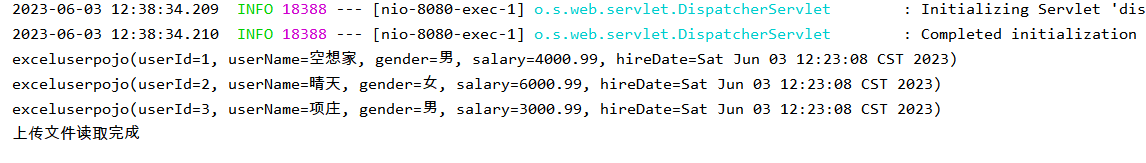
public String uploadexcel(@RequestParam("file") MultipartFile multipartFile) throws IOException {
EasyExcel.read(multipartFile.getInputStream(), exceluserpojo.class, new AnalysisEventListener<exceluserpojo>() {
@Override
public void invoke(exceluserpojo exceluserpojo, AnalysisContext analysisContext) {
System.out.println(exceluserpojo);
}
@Override
public void doAfterAllAnalysed(AnalysisContext analysisContext) {
System.out.println("上传文件读取完成");
}
}).sheet().doRead();
return "上传成功";
}
}
③ 上传html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>上传页面</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="/uploadexcel" enctype="multipart/form-data" method="post" >
<input type="file" name="file">
<input type="submit" value="Excel上传">
</form>
</body>
</html>











Comments | NOTHING