一,Netty的概述和背景
Netty的产生的背景
原生NIO存在的问题:
- NIO的类库和API繁杂,使用较为复杂:需要熟练掌握Selector,ServerSocketChannel,SocketChannel,ByteBuffer等
- 需要具备额外技能:熟悉java多线程,因为NIO编程涉及到Reactor模式,必须对多线程和网络编程非常熟悉,才能编写出高质量的NIO程序
- 开发工作量和难度非常大,例如客户端面临断连重连,网络闪退,半包读写,失败缓存,网络拥堵和异常流的处理……
- JDK NIO的BUG:Epoll Bug,它会导致Selector空轮询,最终导致CPU 100%,直到JDK 1.7版本该问题依旧存在,没有根本解决
netty:基于异步的事件驱动的网络应用框架,它可以高性能的Server和Client
Netty的应用说明:
- Netty是由Jboss提供的一个java开源框架,netty提供异步的,基于事件驱动的网络应用程序框架,用以快速开发高性能的网络IO程序
- Netty可以帮助快速开发,简单的开发一个网络应用,相当于简化和流程化了NIO的开发过程
- Netty是目前最流行的NIO框架,netty在互联网领域,大数据分布式技术领域,游戏行业,通信行业获得了广泛的应用,例如:Hadoop,Dobbo……
Netty的优点:ntty对JDK自带的NIO的API进行了封装,解决了以上问题
- 设计优雅:适用于各种传输类型的统一API,基于灵活可拓展的事件模型,可以清晰的分离关注点,高度可制定的线程模型
- 使用方便:详细记录了javadoc
- 高性能:吞吐量高,延迟小,减少了资源消耗,最小化不必要的内存复杂
- 安全:完整的SSL/TLS和StartTLS支持
- 社区活跃,版本不断在迭代
Netty版本说明:netty版本分为netty3.x,netty4.x,netty5.x
因为Netty5出现重大Bug已经被官网废弃,netty3.x太老,推荐使用Netty4.x的稳定版e
二,netty的线程模型
一,Netty模型的简单概述
Netty主要主从Reactor多线程模型做了一定改进,其中主从Reactor多线程模型有多个Reactor
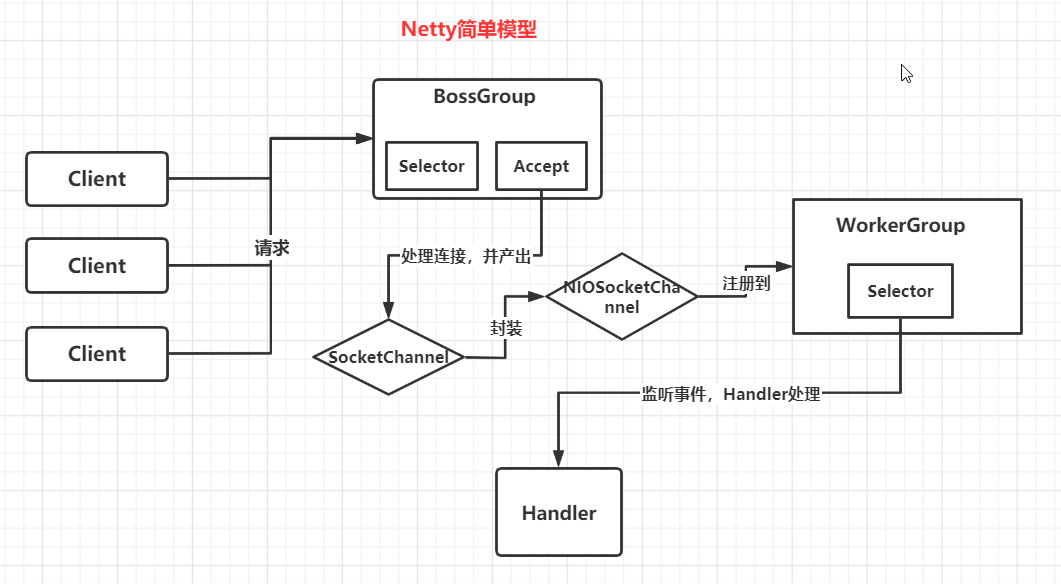
netty用BossGroup和WorkerGroup取代了Reactor中的mainReactor和SubReactor的概念
- BossGroup线程维护Selector,只关注Accept请求
- 当接收Accept请求事件,建立连接并获取对应的SocketChannel对象,并再封装成NioSocketChannel并注册到WorkerGroup线程(worker进行事件循环)维护
- 当Worker线程监听到Selector中有网络读写事件发生,就会交与Handler处理(Handler必须加入通道)
注册:再Reactor中mainReactor只能有一个,当Netty的BossGroup可以有多个

二,Netty模型的详细说明
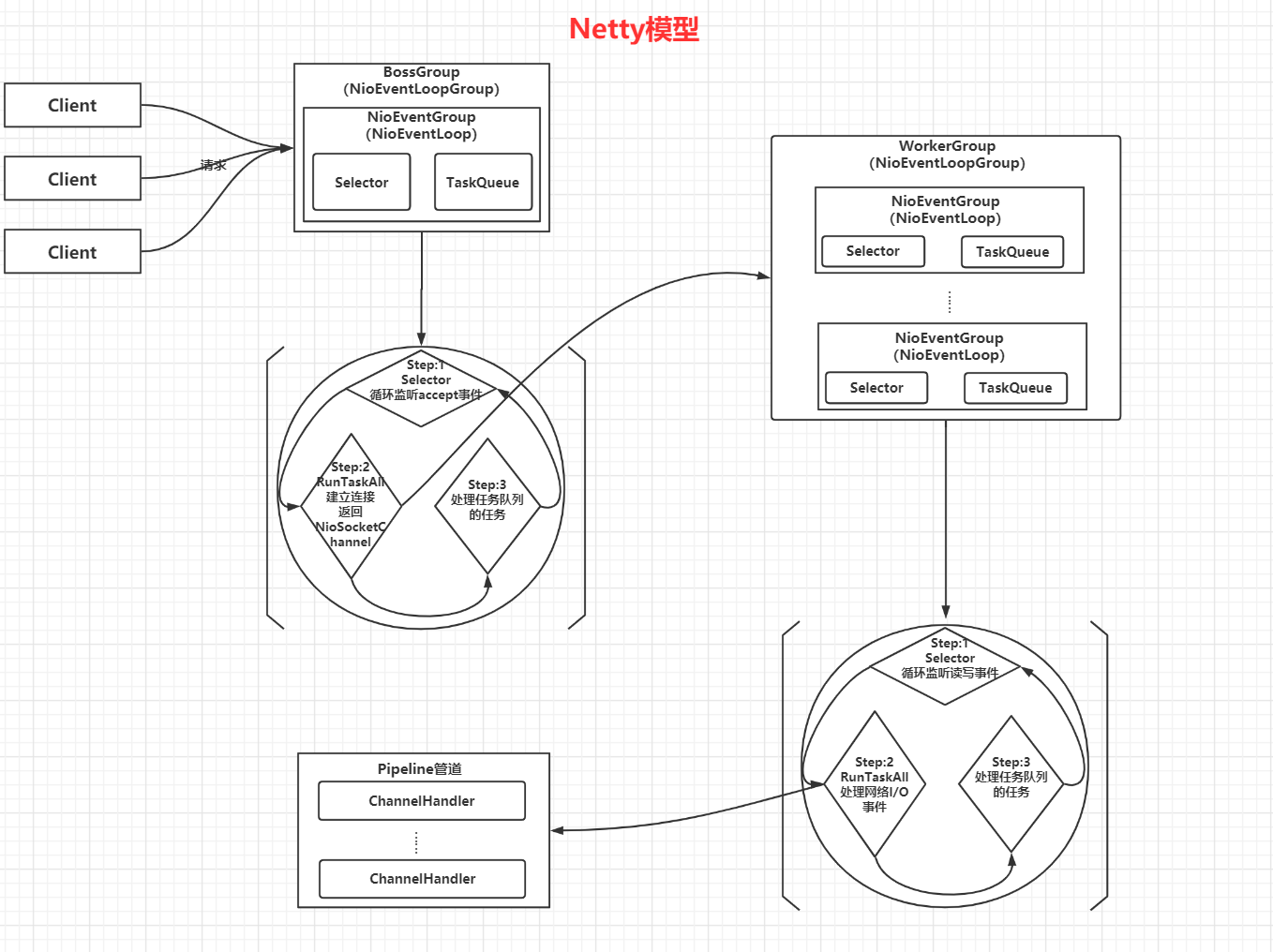
Netty抽象出了两组线程池BossGroup和WorkerGroup:
- BossGroup专门负责接收客户端的连接
- WorkerGroup专门负责网络的读写
Netty模型组件分析:
- BossGroup和WorkerGroup类型都是NioEventLoopGroup
- NioEventLoopGroup相当于一个事件循环组,这个组中含有多个事件循环,每一个事件循环是NioEventLoop
- NioEventLoop表示一个不断循环的执行处理线程,每一个NioEventLoop都有一个Selector,它用于监听绑定在其上的socket的网络通讯
- NioEventLoopGroup可以有多个线程即含有多个NioEventLoop
- 每一个Worker NioEventLoop处理业务时,会使用pipeline管道,pipeline中包含了Channel,通过pipeline可以获取channel通道
- pipeline中维护了很多Handler处理器
Netty组件详细说明:
1,Netty抽象出两组线程池,BossGroup专门负责接收客户端连接,WorkerGroup专门负责网络读写操作
2,EventLoop表示一个不断循环执行处理任务的线程,每一个EventLoop都有独立的Selector,TaskQueue……,用于监听绑定再其上的socket网络通道
3,NioEventLoop内部采用串行化设计,从消息的读取 -> 解码 -> 编码 -> 发送 ,始终由IO线程NioEventLoop负责
- EventLoopGroup下包含多个EventLoop
- 每一个EventLoop中包含一个Selector,一个TaskQueue
- 每一个EventLoop的Selector可以注册多个Channel
- 每一个Channel只会绑定再唯一的EventLoop
- 每一个Channel都绑定有一个自己的ChannelPipeline
注:管道和通道有区别,pipeline管道中包含了通道channel

每个Boss NioEventLoop执行的步骤:分三步
- 轮询accept事件
- 处理accept事件,与client建立连接,生成NioSocketChannel并将其注册到Worker NioEventLoop上的selector进行监听
- 处理任务队列的任务,即runAllTasks
每个Worker NioEventLoop执行的步骤:分三步
- 轮询read,write事件
- 处理I/O事件,即read,write事件,在对应NioSocketChannel处理
- 处理任务队列的任务,即runAllTasks
三,netty的任务队列
任务队列中的Task有3种典型的应用场景
1,用户程序自定义的普通任务
2,用户自定义的定时任务
3,非当前Reactor线程调用Channel的各种用法,例如:在推送系统的业务线程里面,根据用户标识,找到对应的Channel引用,然后调用Writer类方法向该用户推送消息,就会进入到这种场景,最终到任务队列中后被异步消费
任务队列的重要性:
- 假如不加任务队列,线程同步执行,一个任务被堵塞,其他任务全部被堵塞,任务队列可以使任务异步执行
- 任务队列有定时性,可操作性
- 任务队列可以适应多种应用场景,如:消息定点推送
一,无任务队列的同步任务
Netty的Handler处理器
public class handler_netty extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
/*
* 读取实际数据(这里可以读取客户端发来的消息)
* 1,ChannelHandlerContext是上下文对象,它包含有Channel通道和Pipeline管道
* 2,Object msg就是客户端发送的数据,默认是Object
* */
@Override
public void channelRead(final ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
Thread.sleep(10*1000);//堵塞10秒钟
ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("hello,客户端1111\n",CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
System.out.println("gono!!");
}
/*
* 数据读取完毕,回送一个消息
* */
@Override
public void channelReadComplete(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
//writeAndFlush方法是writer和flush两个方法的合并方法
//将数据写入到缓存并刷新
//对发送的数据进行编码
ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("hello,wql你好",CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
}
/*
* 处理异常,一般发生异常关闭通道
* */
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
ctx.close();
}
}
这里有两任务:
1,channelRead方法读取数据
2,channelReadComplete回送数据
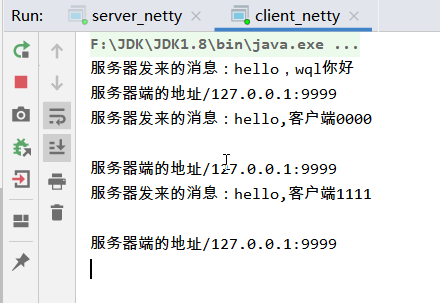
在没有异步任务队列时,channelRead休眠堵塞10秒钟,channelReadComplete也会被堵塞,执行结果是等10秒钟后先执行了channelRead,再执行channelReadComplete

再同步中一个任务线程被堵塞,所以的任务都被堵塞
二, 自定义的普通任务队列TaskQueue
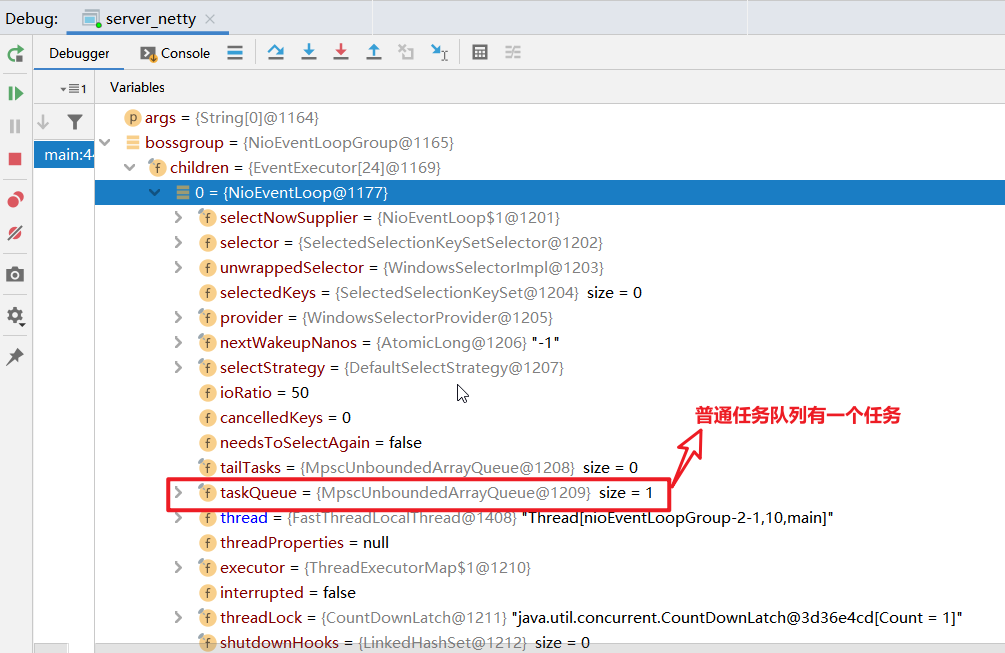
使用Netty中Chennel调用EventLoop中线程池对象,将任务加入到队列中,上下文对象ChannelHandlerContext调用Channel通道,使用 execute将任务提交到TaskQueue中
public class handler_netty extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void channelRead(final ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
//自定义任务队列
ctx.channel().eventLoop().execute(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
try {
//将执行的操作翻入队列中执行
Thread.sleep(10*1000);
ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("hello,客户端0000\n",CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
System.out.println("gono!!");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}}
});}
@Override
public void channelReadComplete(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("hello,wql你好",CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
ctx.close();
}}
执行结果:这个时候被堵塞的channelRead后被执行,先执行channelReadComplete任务

Dubug看TaskQueue是否有任务:

三,自定义的定时任务队列scheduledTaskQueue
使用Netty中Chennel调用EventLoop中线程池对象,将任务加入到定时队列中,上下文对象ChannelHandlerContext调用Channel通道,使用 schedule将任务提交到TaskQueue中
方法:ctx.channel().eventLoop().schedule(new Runnable() {},Time,TimeUnit);
schedule方法有三个参数分别是:new Runable(),时间,时间单位
public class handler_netty extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void channelRead(final ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
//定义定时任务队列
//将任务提交到定时任务scheduledTasQueue队列中
ctx.channel().eventLoop().schedule(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
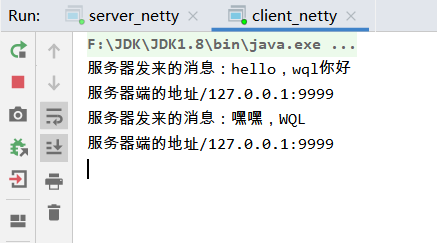
ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("嘿嘿,WQL",CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
System.out.println("gono!!");
}
},10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
/*
* 数据读取完毕,回送一个消息
* */
@Override
public void channelReadComplete(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
//writeAndFlush方法是writer和flush两个方法的合并方法
//将数据写入到缓存并刷新
//对发送的数据进行编码
ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("hello,wql你好",CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
}
/*
* 处理异常,一般发生异常关闭通道
* */
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
ctx.close();
}}
执行结果: channelRead先定时堵塞10秒再执行,channelReadComplete先执行

四,异步模型Future机制
异步模型的基本介绍:
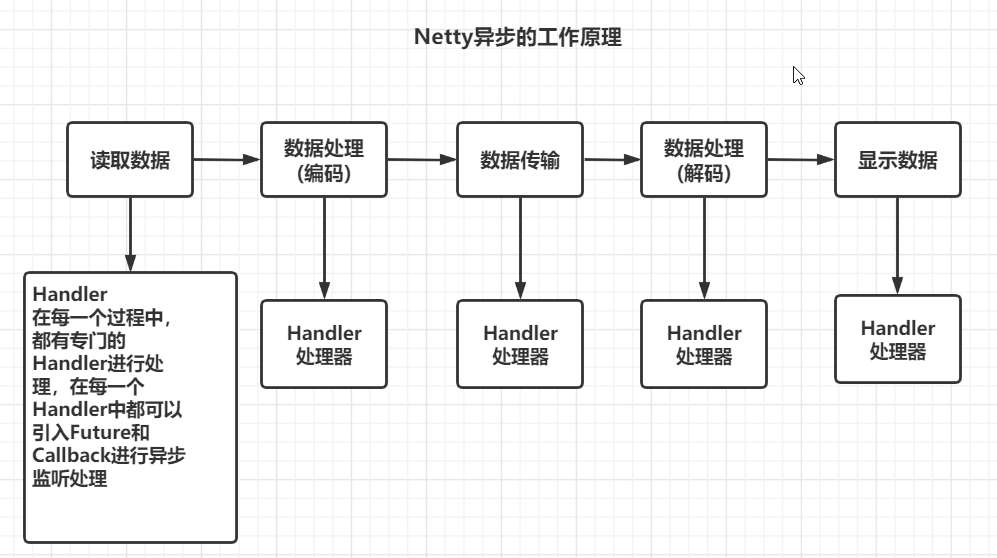
1),异步的概念和同步相对,当一个异步过程调用发出后,调用者不能立刻等待结果,实际处理这个调用的组件再完成后,通过状态,通知和回调来通知调用者
2),Netty中的I/O操作是异步的,包括Bind,Writer,Connect等操作会简单的返回一个ChannlFuture
3),调用者并不能立即获得结果,而是通过Future-Listener机制,用户可以方便的主动获取或者通过机制获得I/O操作和结果
4),Netty的异步模型是建立在Future和Callback的之上的,callback就是回调,重点说Future,它的核心思想是:假设一个方法wql,计算过程可能非常耗时,等待wql返回肯定不合适,那么可以在调用wql的时候,里面返回一个Future,后面可以通过Future去监控方法wql的处理过程(即:Future-Listener)
一,Future机制
future的说明:
- 表示异步的执行结果,可以通过它提供的方法来检测执行是否完成
- Future的子接口ChannelFuture,可以在其他添加监听器,当监听的事件发生时,就会通知到Future
netty框架的目标就是让你的业务逻辑从网络基础应用编码中分离处理
工作原理图:

二,Future的API介绍
netty的Future本身继承了concurrent并发包中的Future
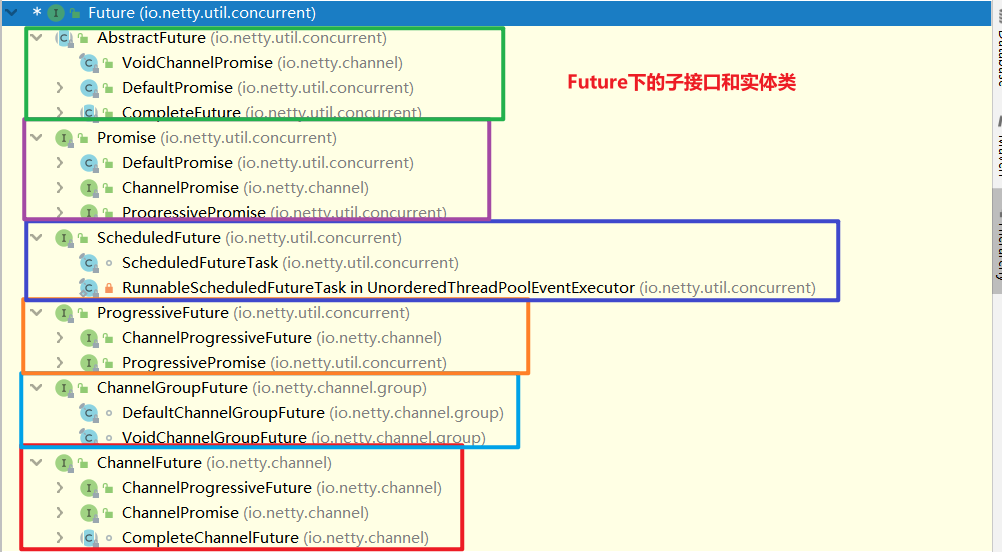
public interface Future<V> extends java.util.concurrent.Future<V> {
在netty的Future中,它是一个顶级接口,下面有我们众多的子接口和实例类
我们通常用ChannelFuture,API以Future和ChannelFuture为例

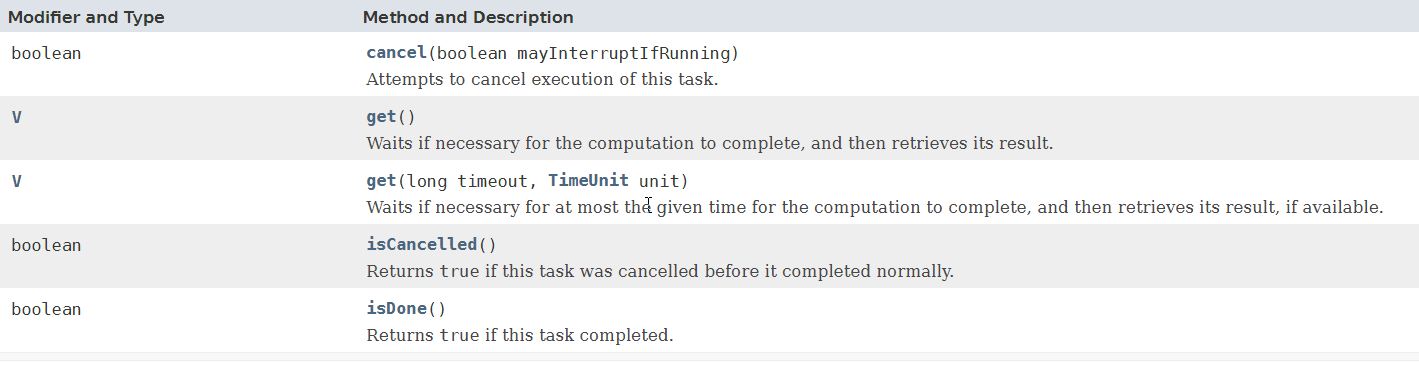
Future的API:
isDone():判断当前操作是否完成
isCancelled():判断已完成的当前操作是否被取消
cancel():取消任务执行
get():等待计算完成在获取检索的结果
get(time,timeunit):给定时间和时间单位,来获取结果

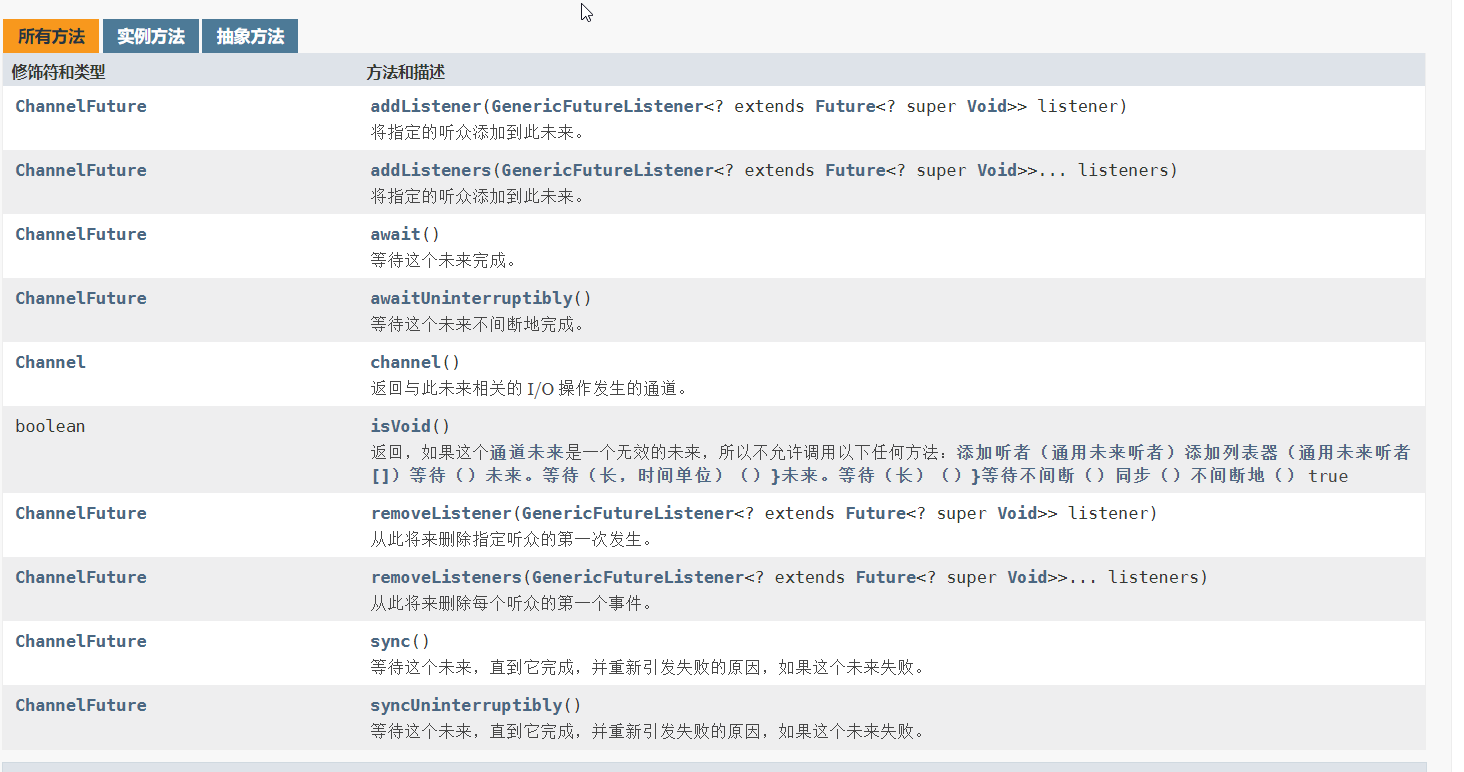
ChannelFuture的API:
sync():等待这个任务,直到它完成,同步操作
addListener():注册监听器,当任务操作完成,会通知监听器,如Futuer对象完成将会通知指定监听器
isSuccess():判断已完成的当前操作是否成功
getCause():获取已知当前操作失败的原因
channel():获取Channel对象
……

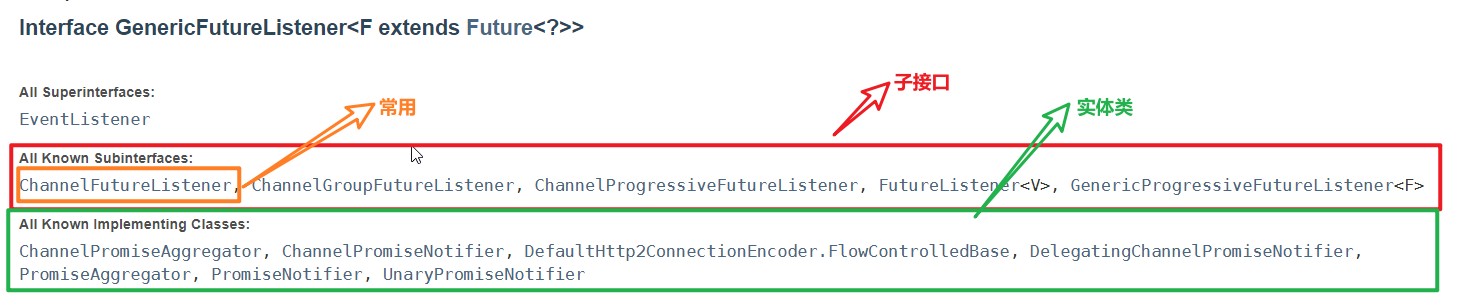
三,Future的监听对象GenericFutureListener
在Netty中提供了专门针对监听的监听对象GenericFutureListener
GenericFutureListener下的子接口和实体类

GenericFutureListener只有一个方法:
operationCompleta():监听的逻辑

Future-Listener案例:给ChannelFuture channelFuture = serverBootstrap.bind(9999).sync()绑定监听
//服务器对象绑定端口并同步,生成一个ChannelFuture对象
ChannelFuture channelFuture = serverBootstrap.bind(9999).sync();
//绑定监听
channelFuture.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture channelFuture) throws Exception {
//监听绑定是否成功
Boolean A = channelFuture.isSuccess();
if(A){
System.out.println("端口绑定成功!!");
}else {
System.out.println("端口绑定失败!!");
}
}
});
结果:

五,netty案例
要求:基于netty实现简单的客户端和服务器端通信
dome主要有四个class
Server类:
public class server_netty {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
//创建BossGroup和WorkerGroup两个线程循环组
//创建BossGroup只处理连接请求
EventLoopGroup bossgroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
//创建WorkerGroup处理具体业务
EventLoopGroup workergroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
//创建服务器的启动对象,配置参数
ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
//使用链式编程来设置BootStrap服务器启动对象的参数配置
try {
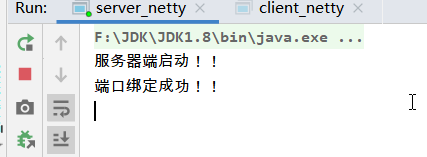
System.out.println("服务器端启动!!");
serverBootstrap.group(bossgroup,workergroup)//设置两个线程组
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)//使用NioSocketChannel作为服务器的通道实现
.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 128)//设置线程队列等待连接的个数
.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true)//设置保持活动的连接状态
.childHandler(
//创建一个通道测试对象,匿名对象创建
new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
//给pipeline设置处理器ChannelHandler
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
System.out.println("客户对应的SocketChannel:"+socketChannel.hashCode());
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new handler_netty());//添加自定义处理器
}
});//给WorkerGroup的EventLoop对应的管道设置处理器
//服务器对象绑定端口并同步,生成一个ChannelFuture对象
ChannelFuture channelFuture = serverBootstrap.bind(9999).sync();
//绑定监听
channelFuture.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture channelFuture) throws Exception {
//监听绑定是否成功
Boolean A = channelFuture.isSuccess();
if(A){
System.out.println("端口绑定成功!!");
}else {
System.out.println("端口绑定失败!!");
}
}
});
//对关闭通道进行监听
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
}finally {
bossgroup.shutdownGracefully();
workergroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
ServerHandler类:
public class handler_netty extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
/*
* 读取实际数据(这里可以读取客户端发来的消息)
* 1,ChannelHandlerContext是上下文对象,它包含有Channel通道和Pipeline管道
* 2,Object msg就是客户端发送的数据,默认是Object
* */
@Override
public void channelRead(final ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
//定义定时任务队列
//将任务提交到定时任务scheduledTasQueue队列中
ctx.channel().eventLoop().schedule(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("嘿嘿,WQL",CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
System.out.println("gono!!");
}
},10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
/*
* 数据读取完毕,回送一个消息
* */
@Override
public void channelReadComplete(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
//writeAndFlush方法是writer和flush两个方法的合并方法
//将数据写入到缓存并刷新
//对发送的数据进行编码
ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("hello,wql你好",CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
}
/*
* 处理异常,一般发生异常关闭通道
* */
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
ctx.close();
}
}
Client类:
public class client_netty {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
//客户端只需要一个线程循环组
EventLoopGroup eventExecutors = new NioEventLoopGroup();
//创建客户端启动对象
//注:服务器端用ServerBootStrap,客户端用BootStrap
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
try{
//设置参数
bootstrap.group(eventExecutors)//设置线程组
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)//设置客户端通道的实现类,反射
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
//加入自己的处理器
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new handlerclient_netty());
}
});
//启动客户端去连接服务器端
ChannelFuture sync = bootstrap.connect("127.0.0.1", 9999).sync();
//对关闭通道进行监听
sync.channel().closeFuture().sync();
}finally {
eventExecutors.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
ClientHandler类:
public class handlerclient_netty extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
//当通道就绪就会触发该方法
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("Hello 大佬你好", CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
}
//当通道有读取事件时,会触发
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
ByteBuf byteBuf = (ByteBuf) msg;
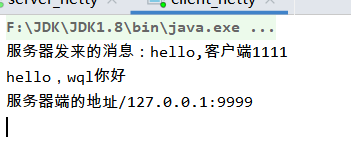
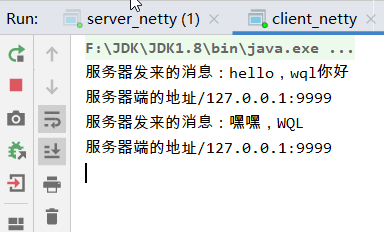
System.out.println("服务器发来的消息:"+byteBuf.toString(CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
System.out.println("服务器端的地址"+ctx.channel().remoteAddress());
}
//处理异常
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
cause.printStackTrace();
ctx.close();
}
}
结果:

六,基于netty的webSocket通信小案例
要求:
1)Http协议是无状态的,浏览器和服务器间请求响应一次,下一次会重新创建连接
2)实现基于WebSocket的长连接全双工的交互
3)改变Http协议多次请求的约束,实现长连接,服务器可以发送消息给浏览器
4)客户端和浏览器会互相感知,比如服务器关闭,浏览器会感知到,同样浏览器关闭,服务器也会感知到
这个案例对实际的开发挺有用的
Srever端:
public class websocket_server_netty {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建BoosEventLoopGroup和WorkerEventLoopGroup两个池对象
EventLoopGroup BoosEventLoopGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1);//指定线程池中的线程个数
EventLoopGroup WorkerEventLoopGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();//默认线程池中线程个数是CPU核数*2
//服务对象
ServerBootstrap bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
//配置参数
try {
bootstrap.group(BoosEventLoopGroup,WorkerEventLoopGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
//获取pipeline
ChannelPipeline pipeline = socketChannel.pipeline();
//使用http的编码和解码器
pipeline.addLast(new HttpServerCodec());
//以块的方式写,添加ChunkedWrite处理器
pipeline.addLast(new ChunkedWriteHandler());
/*http数据在传输过程中是分段的,HttpObjectAggregator可以将多个段聚合
这就是为什么当浏览器发送大量数据时,就会发出多次http请求
*/
pipeline.addLast(new HttpObjectAggregator(8192));
/*对应webSocket,它的数据是以帧(frame)的形式传递
*WebSocketFrame 下面有六个不同类型的帧的处理类
* 浏览器请求时 ws://localhost:9999/xxx 表示请求url
* WebSocketServerProtocolHandler核心功能是将http协议升级为WS协议,保持长连接
* */
pipeline.addLast(new WebSocketServerProtocolHandler("/hello"));
//自定义Handler,处理业务逻辑
pipeline.addLast(new websocket_handler());
}
});
//配置端口,
ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.bind("127.0.0.1", 9999).sync();
future.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
BoosEventLoopGroup.shutdownGracefully();
WorkerEventLoopGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
ServerHandler:
//TextWebSocketFrame 表示一个文本帧(frame)
public class websocket_handler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<TextWebSocketFrame> {
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext, TextWebSocketFrame textWebSocketFrame) throws Exception {
System.out.println("服务器收到消息:"+textWebSocketFrame.text());
//回复消息
channelHandlerContext.channel().writeAndFlush(new TextWebSocketFrame("[服务器时间] "+ LocalDateTime.now()+" \n"+textWebSocketFrame.text()));
}
@Override
public void handlerAdded(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
//id是唯一的值,LongText是唯一的ShorText不是唯一的
System.out.println("handlerAdded被调用"+ctx.channel().id().asLongText());
System.out.println("handlerAdded被调用"+ctx.channel().id().asShortText());
}
@Override
public void handlerRemoved(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
System.out.println("handlerRemoved被调用"+ctx.channel().id().asLongText());
System.out.println("handlerRemoved被调用"+ctx.channel().id().asShortText());
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
ctx.close();
}
}
写一个HTML用Dom中websocket与后端通信:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<script>
var socket;
if(window.WebSocket){
socket =new WebSocket("ws://localhost:9999/hello");
socket.onmessage =function (ev) {
var s= document.getElementById("responsetext");
s.value=s.value+"\n"+ev.data;
}
socket.onopen =function (ev) {
var wql = document.getElementById("responsetext");
wql.value="连接开启!";
}
socket.onclose =function (ev) {
var wql = document.getElementById("responsetext");
wql.value="连接关闭!";
}
}else {
alert("当前浏览器不支持websocket")
}
function send(message) {
if(socket.readyState==WebSocket.OPEN){
socket.send(message)
}else {
alert("连接没有开启")
}
}
</script>
<body>
<form onsubmit="return false">
<textarea name="FQ" style="height: 200px ;width: 200px"></textarea>
<input id="wql" type="button" value="发送消息" onclick="send(this.form.FQ.value)">
<textarea id="responsetext" style="height: 200px;width: 200px"></textarea>
<input type="button" value="情空内容" onclick="document.getElementById('responsetext').value=''">
</form>
</body>
</html>
结果:







Comments | NOTHING